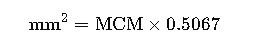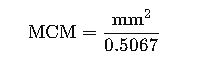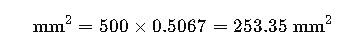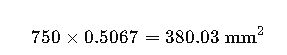Accurate MCM to mm² conversion is essential for professionals handling international electrical design and installations.
IEC and NEMA standards require precise sizing to ensure safety, compatibility, and regulatory electrical system compliance.
MCM ↔ mm² Conversion Calculator
Extensive MCM to mm² Conversion Table (IEC/NEMA Standards)
The following table lists common MCM values and their equivalent in square millimeters (mm²), rounded to industry-standard precision. These values are essential for engineers working across metric and imperial electrical frameworks.
| MCM (kcmil) | mm² (approx.) | Standard Use Case Example |
|---|---|---|
| 14 MCM | 7.10 mm² | Small lighting circuits (NEMA) |
| 18 MCM | 9.12 mm² | Small motors, branch circuits |
| 20 MCM | 10.15 mm² | Residential subfeeds |
| 30 MCM | 15.23 mm² | HVAC systems |
| 40 MCM | 20.30 mm² | Feeders for mid-size panels |
| 50 MCM | 25.37 mm² | Parallel conductors, solar DC |
| 60 MCM | 30.45 mm² | Commercial feeders |
| 70 MCM | 35.52 mm² | Transformer primary cabling |
| 75 MCM | 38.06 mm² | Large air handlers |
| 100 MCM | 50.74 mm² | 3-phase panel mains |
| 125 MCM | 63.42 mm² | Generator leads |
| 150 MCM | 76.11 mm² | Switchgear connections |
| 175 MCM | 88.79 mm² | UPS distribution |
| 200 MCM | 101.48 mm² | Industrial process panels |
| 250 MCM | 126.85 mm² | Large building mains |
| 300 MCM | 152.22 mm² | Feeder to main distribution |
| 350 MCM | 177.59 mm² | Bus duct tap-offs |
| 400 MCM | 202.96 mm² | Transformer secondaries |
| 500 MCM | 253.71 mm² | Large motors |
| 600 MCM | 304.45 mm² | High-capacity mains |
| 700 MCM | 355.19 mm² | Utility interface wiring |
| 750 MCM | 380.56 mm² | Heavy-duty distribution |
| 800 MCM | 405.93 mm² | Parallel cabling arrays |
| 900 MCM | 456.67 mm² | Substation feeders |
| 1000 MCM | 507.42 mm² | Industrial control centers |
| 1250 MCM | 634.27 mm² | High-rise service entries |
| 1500 MCM | 761.13 mm² | Utility-grade interconnects |
| 1750 MCM | 887.98 mm² | Mining power cables |
| 2000 MCM | 1014.84 mm² | Heavy transmission |
| 2500 MCM | 1268.55 mm² | Utility-scale solar/wind |
| 3000 MCM | 1522.26 mm² | Inter-grid connections |
Note: Conversion is not exact due to rounding and different copper construction (stranded vs solid), insulation, and manufacturer tolerances. Always consult the official IEC 60228 and NEC/NEMA tables for certification-compliant sizing.
MCM to mm² Conversion Formulas
MCM (also called kcmil or “thousands of circular mils”) and mm² are related by the geometry of their respective unit systems.
Primary Conversion Formula
The fundamental formula to convert from MCM to mm² is:
Reverse Conversion Formula
To convert from mm² to MCM:
Explanation of Variables
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| MCM (or kcmil) | Thousands of circular mils. Used in NEMA/NEC wire gauges. |
| mm² | Square millimeters, the SI unit of cross-sectional area per IEC 60228. |
| 0.5067 | Constant derived from the ratio between one circular mil and one square millimeter. Based on: 1 MCM = 1,000,000 circular mils = 0.5067 mm². |
Background on Units
- Circular mil is the area of a circle with a diameter of one mil (0.001 inch).
- MCM (kcmil) simplifies large circular mil values (e.g., 500,000 CM = 500 MCM).
- Square millimeter is the SI-compliant measure of area based on metric dimensions.
Real-World Use Case #1: Industrial Substation Conversion
Problem:
An industrial substation in the U.S. is being expanded to support metric-based European machinery. The existing feeder cables are 500 MCM. The new IEC-spec transformers require wire sizing in mm² for terminal lugs.
Solution:
Using the formula:
The team selects 240 mm² IEC-class conductors (next IEC standard size) to ensure mechanical compatibility and match ampacity. The conductor must also meet the derating factors for ambient temperature per IEC 60364.
Result:
Compliance is achieved with minimal infrastructure modification. The conversion calculator enabled accurate, regulation-compliant cable selection between NEC and IEC systems.
Real-World Use Case #2: Solar PV Plant Interconnection (IEC + NEMA Hybrid)
Scenario:
A utility-scale solar PV farm in Chile is integrating North American inverter systems (MCM-rated outputs) into an IEC-regulated national grid. The cable exit from each inverter is 750 MCM.
Conversion:
The closest matching IEC cable is 400 mm² copper.
However, to comply with local regulations (and allow for 90°C continuous ampacity), derating tables are consulted, and 500 mm² cable is used to accommodate potential thermal buildup.
Implementation Notes:
- Temperature Correction Factors: Required per IEC 60287.
- Mechanical Compatibility: Lug adapters installed for MCM terminations on IEC-rated busbars.
- Standards Cross-reference: Verified via UL 486A-B and IEC 61238-1.
Common Applications for Cross-Standard Conversion
- Multinational Equipment Installations
- Import/Export Electrical Engineering
- Utility-Scale Interconnection Projects
- Transformer Feeder Adaptation
- Maritime & Offshore Systems (ISO/IEC/NEMA hybrids)
Tips for Using MCM to mm² Conversion in Practice
- Always Round Up to the nearest IEC standard mm² size.
- Consider Stranded vs. Solid — conductor construction affects effective cross-sectional area and heat dissipation.
- Check Ampacity Equivalence — don’t assume mm² wire has the same ampacity as the MCM size.
- Use Manufacturer Tables — especially for high-precision applications or when dealing with aluminum vs copper.
- Regulatory Cross-Check — local codes may require both NEC and IEC compliance for certification.
Trusted References and Further Reading
- IEC 60228: Conductors of Insulated Cables
- NFPA 70®: National Electrical Code® (NEC)
- NEMA Wire Ampacity Charts
- UL White Book – Electrical Conductors
- IEC 60364 Electrical Installations for Buildings
Recommended Practices for Engineers
- Always check the final application: Thermal, mechanical, and electrical constraints must all align.
- Refer to local code and equipment: Even within the same country, localities or utility providers might enforce stricter rules.
- Ensure terminal compatibility: Mismatches in size-to-lug fittings can compromise safety.
- Use derating charts properly: Altitude, ambient temperature, and grouping affect current-carrying capacity.
- Confirm approvals: UL, IEC, or CE marking may be necessary for cross-border installations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between MCM and kcmil?
There is no difference. Both terms refer to “thousands of circular mils.” MCM is the older term, while kcmil is now more standard in engineering documentation.
Is there a standard table for converting MCM to mm²?
No universal legal standard exists, but the formula 1 MCM = 0.5067 mm² is widely accepted based on the geometry of a circular mil. Standardized charts like the one in this article are derived from this formula.
Why can’t I just match mm² by number?
Because 1:1 area doesn’t mean 1:1 ampacity. IEC and NEC calculate ampacity using different assumptions. For instance, 250 MCM ≈ 127 mm², but it does not always carry the same current as 120 mm² or 150 mm² in IEC systems.
Can I use this for aluminum conductors?
Yes, but note that aluminum has ~61% the conductivity of copper, so equivalent ampacity requires larger cross-sectional area. Derate accordingly and check manufacturer specs.
Where can I find full ampacity values?
Final Thoughts
Whether you’re specifying feeder cables for a transformer or adapting European panels to U.S. infrastructure, a reliable MCM to mm² Conversion Calculator bridges the metric-imperial gap. This ensures electrical safety, regulatory compliance, and mechanical compatibility—essential in a globalized engineering environment.
Professionals operating in multinational construction, renewable energy, OEM manufacturing, and mission-critical systems should integrate conversion tools directly into their workflows, ensuring consistent, precise decisions.