Convert Watts to Amps Easily with Our Calculator Using Formulas and Electrical Tables.
Learn about electrical protections, breakers, cables, and overloads by applying power factors and making quick conversions.
How to Calculate an Electrical Circuit: Breakers, Cables, and Terminals
Example Calculation:
- TV: 450 watts at 120 volts
- Computer: 350 watts at 120 volts
- Fan: 500 watts at 120 volts
Step 1: Calculate the Total Circuit Power
First, add up the power of all the devices:

Step 2: Calculate the Circuit Amperage
Next, convert the total power to amperage using the formula:
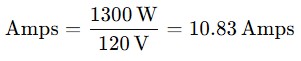
Step 3: Select Breakers and Cables
Breaker: Refer to Table 1 and choose the next highest breaker above 10.83A: a 15A breaker.
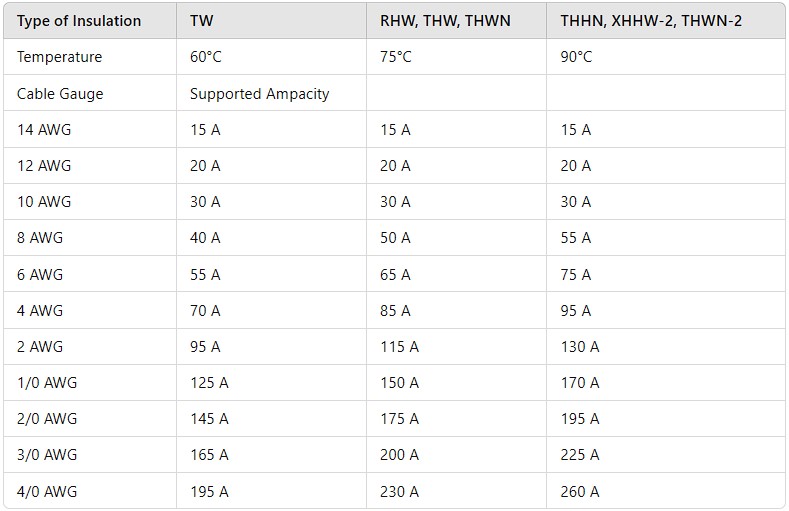
Wiring: According to the NEC (Table 2), use 14 AWG wire at 60ºC for a 15A breaker.
The NEC/NTC2050 requires that for currents under 100A, 60ºC-rated wire must be used, and for currents over 100A, 75ºC-rated wire is necessary.
Table 1. Nominal Breaker Ratings

Table 2. Nominal Cable Ratings
How to Fix a Tripping Breaker Problem
If a 15-amp breaker trips when you turn on a 2000-watt microwave, it’s likely that the microwave is overloading the circuit.
This happens because the current drawn by the appliance exceeds the breaker’s capacity.
How to Identify the Problem:
Step 1: Calculate the Appliance’s Amperage
To determine if the microwave is overloading the circuit, calculate the amperage using the following formula:

For example, if the microwave uses 2000 watts and operates on a standard 120-volt circuit:
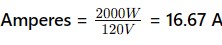
Step 2: Compare the Amperage with the Breaker Rating
The microwave draws 16.67 amps, while the breaker is rated for 15 amps. This mismatch causes the breaker to trip.
Solution: Replace the Breaker and Wiring
Replace the 15-amp breaker with a 20-amp breaker to handle the microwave’s power consumption.
Additionally, upgrade the wiring to accommodate the higher amperage of the new breaker.
How to Check If a Device Can Be Plugged Into an Outlet
When considering purchasing a new electrical device, such as a 220V oven, it is crucial to ensure that it can safely connect to an outlet in your home. Here’s how to verify compatibility:
1. Check the Device’s Voltage and Power
For example, the oven has the following specifications:
- Voltage: 220V
- Power: 3500W
2. Examine Your Home’s Circuit
To ensure the kitchen circuit is compatible, verify:
- Circuit Voltage: It should match the device’s voltage (220V).
- Breaker Amperage: The circuit breaker in the kitchen’s electrical panel must be suitable for the device’s consumption.
In this scenario, the kitchen has a 15-amp protection.
3. Calculate the Device’s Amperage Consumption
To determine if the oven can be plugged in, calculate its amperage consumption using the formula:
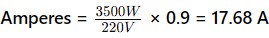
4. Compare with Circuit Capacity
The oven’s consumption is approximately 17.68 amps, whereas the kitchen circuit protection is 15 amps.
Solutions:
- Choose a Different Device: Look for an oven with lower power consumption that uses less than 15 amps.
- Upgrade the Circuit: Increase the wiring capacity and breaker protection in the kitchen to handle higher amperage.
How to Check if a Three-Phase Motor is Operating Correctly
To ensure a three-phase motor is functioning properly in an industrial setting, it’s crucial to measure the current and compare it with the calculated value. Here’s how you can perform this check with an example.
Example of a Three-Phase Motor:
- Motor Power: 3000 W
- Operating Voltage: 460 V
- Power Factor (P.F.): 0.85
- Measured Current with Multimeter: 10 A
Step 1: Calculate the Expected Current
To determine if the motor is operating normally, calculate the theoretical current using the formula for three-phase systems:
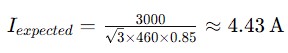
Step 2: Compare Calculated Current with Measured Current
- Calculated Current: 4.43 A
- Measured Current: 10 A
Conclusion:
The measured current is significantly higher than the calculated current. This discrepancy indicates that the motor is operating outside normal parameters, suggesting a potential issue that needs to be investigated and repaired.
How Many Devices Can You Connect to an Electrical Circuit?
To determine how many devices you can connect to an electrical circuit, follow these steps. We’ll use an example of a 20A circuit with 12 AWG wiring and devices operating at 120V.
Devices to Connect:
- Television: 200 W
- DVD Player: 300 W
- Coffee Maker: 1000 W
- Microwave: 900 W
Step 1: Sum the Power Ratings
First, calculate the total power by adding up the watts of all devices:
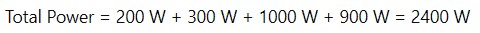
Step 2: Calculate the Total Amperage
Next, convert the total power from watts to amperes using the formula:

Since the total amperage calculated (22.2 A) exceeds the circuit’s maximum capacity of 20A, you cannot connect all these devices to the same circuit.
How Many 180W Devices Can You Connect to an Electrical Circuit?
f you have a 20-amp circuit breaker, you can determine how many 180W devices can be connected to it. Follow these steps to find out:
Step 1: Calculate the Current Draw of Each Device
For a 180W device operating at 120V with a power factor of 1:
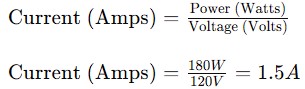
Step 2: Determine the Number of Devices You Can Connect
Next, divide the circuit breaker’s capacity by the current draw of each device:
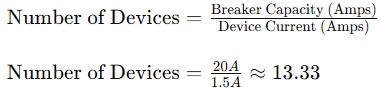
This means you can connect up to 13 devices of 180W each to the same circuit without overloading it.
Formulas for Watts to Amperes: Single-Phase, Two-Phase, Three-Phase, and DC
Single-Phase, Two-Phase, and Three-Phase (AC) Formulas:

Formula (DC):
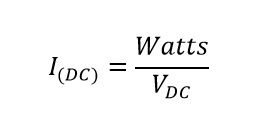
Key Terms:
- Power Factor (FP): Measures how efficiently a device uses energy. It shows the real power consumed in watts. If unknown, use a standard reference value.
- Watts: The unit of power indicating the actual energy consumed by electrical equipment.
- Line-to-Neutral Voltage (V_L-N): The voltage in single-phase systems, often used in homes. Convert V_L-N to Line-to-Line Voltage (V_L-L) using the appropriate formula.
- Line-to-Line Voltage (V_L-L): Common in three-phase systems and found on equipment nameplates. Convert V_L-L to Line-to-Neutral Voltage (V_L-N) with the correct formula.
- Direct Current Voltage (V_DC): Voltage used in DC systems.
- AC Current (I_AC): The current for single-phase, two-phase, or three-phase AC systems.
To convert, transform, or calculate from watts to amps quickly, follow these steps
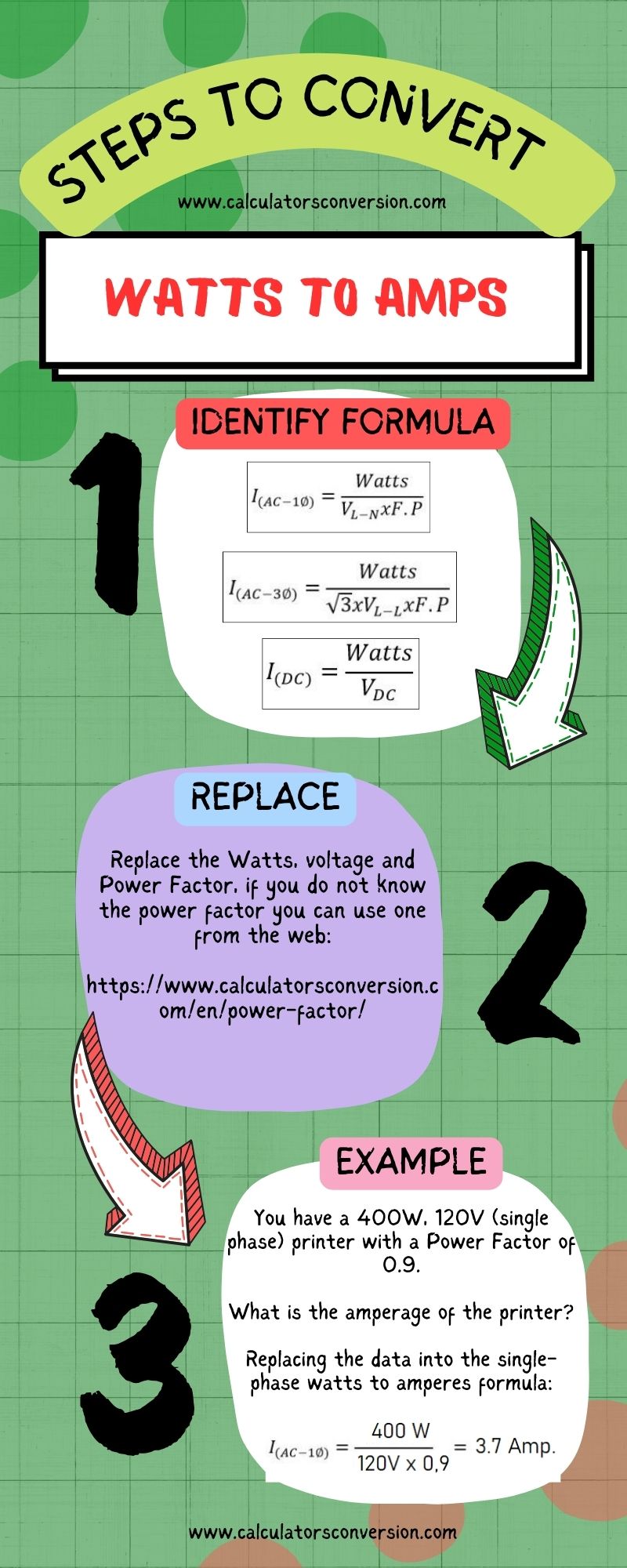
Step 1, identify formula:
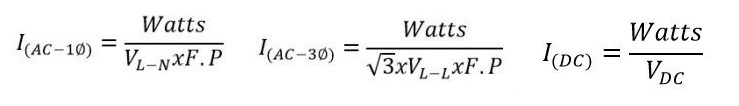
Step 2, replace:
Replace the Watts, Voltage and Power Factor, if you don’t know the power factor you can use one of these common power factors.
Step 3, example:
You have a 400W, 120V (single phase) printer with a Power Factor of 0.9. What is the amperage of the printer?
Replacing the data into the single-phase watts to amperes formula:
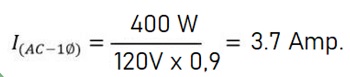
Tables of equivalences of watts (Watts) to amperes
Single-phase watts to amps table
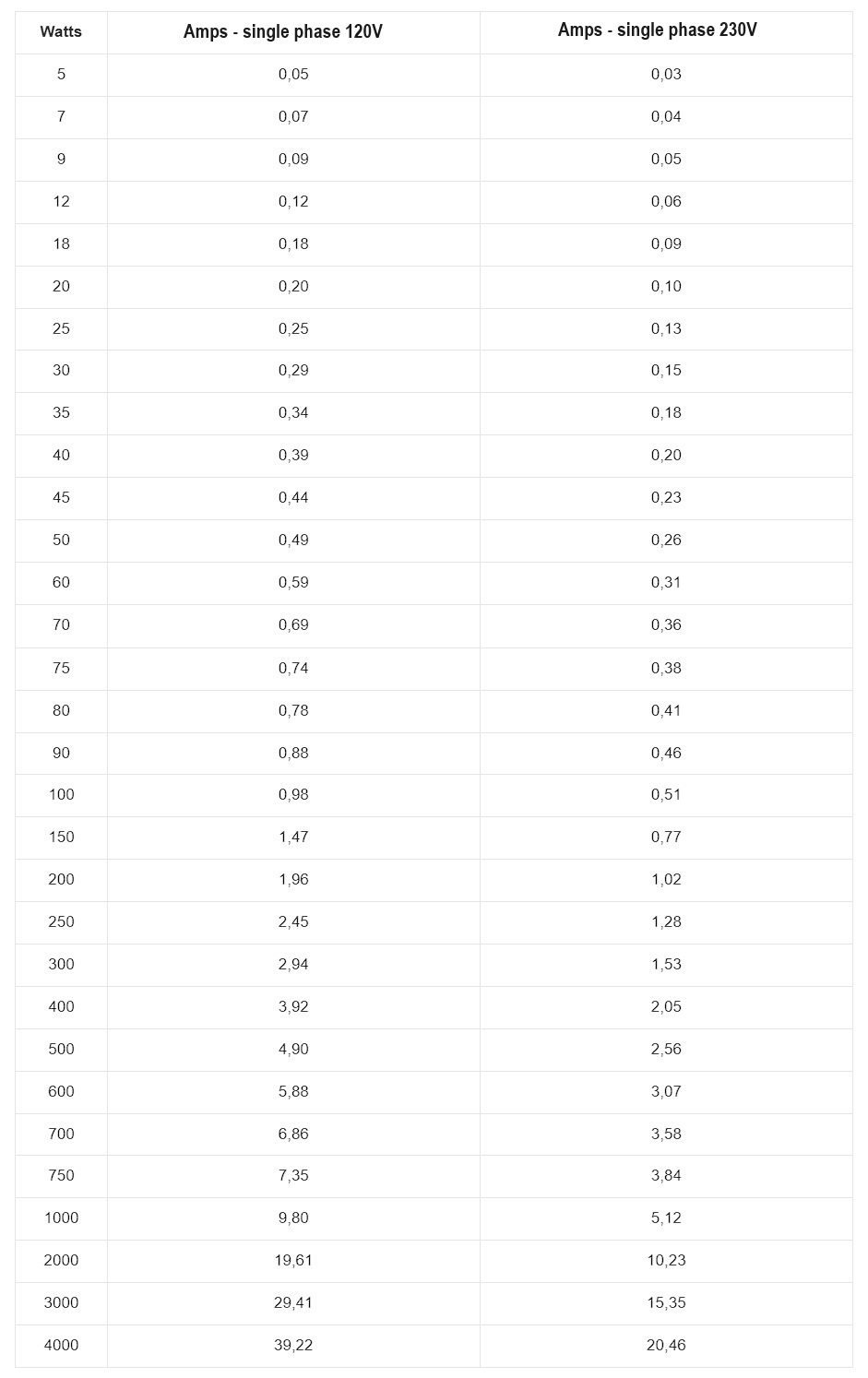
In the previous table a power factor of 0.85 is considered.
Table to transform watts into three-phase amperes
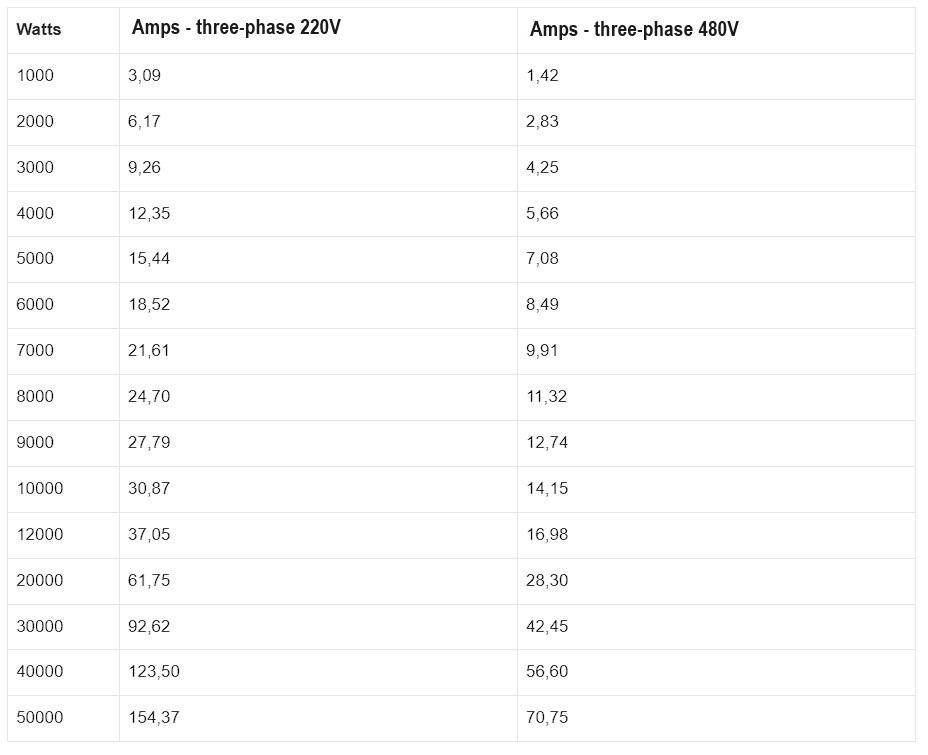
The power factor considered in the previous table is 0.85.
Examples of watts to amp
Example 1, A refrigerator consumes 3000W, how many amps is it equivalent to?
If the refrigerator is connected to 120V and assuming a power factor of 0.9, the answer would be 27.78 Amps.
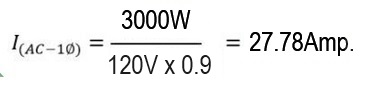
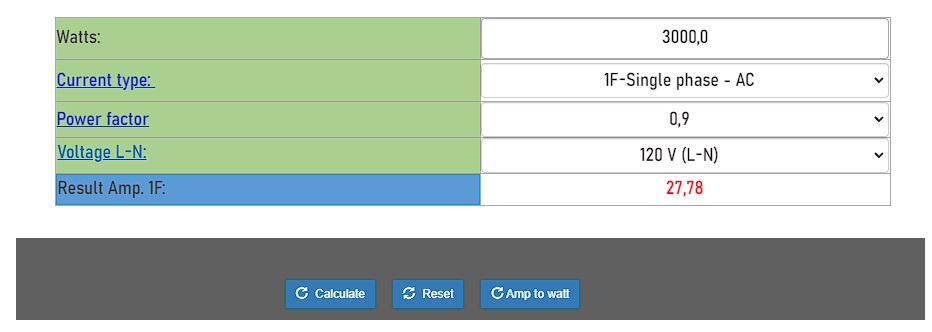
The other way to convert is to perform the calculation automatically with the watts to amps calculator:
Example 2, How many amps does a washing machine and dryer consume in 5000W?
If the dryer is connected to 220V the amperage would be 25 Amps, assuming a power factor of 0.9.
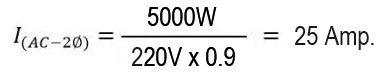
Important! In this example, a line-to-line voltage of 220V was considered , which is why the two-phase formula was used; however, if the connection is single-phase, the single-phase formula must be used.
Example 3, How many amperes is equivalent to 8000W three-phase circular saw connected to 460V?
In this case, the three-phase watts to amperes formula is used, therefore the amperage is: 11.16 Amperes with a power factor of 0.9.
Important!
In three-phase equipment, the power factor is very important, therefore it must be verified in each equipment; if it is not available, it can be estimated with the power factor table .
Most common conversions:
The equivalence of 1 watts in amps:
There are several answers for this conversion depending on the type of AC or DC current, power factor etc, however the simplest answer is 0.01 Amps, for AC voltage, power factor equal to 1 and 120V voltage.
How many amps are 1000 Watts:
The simplest answer will be 8.33 Amp with an AC voltage, a power factor of 1 and a voltage of 120V.
1500 Watts how many amps are:
Like the previous 1500Watts conversion are 12.5 Amps, with an AC voltage, a fp of 1, a single phase voltage of 120V.
600 Watts to how many amps is equivalent:
They are 5 single phase AC amps, with a voltage of 120 V and a power factor of 1.
2000 Watts to how many amps is equivalent:
The equivalence is 16.67 single phase amps of 120Volt AC, a power factor of 1.
Definitions of watts, amps and volts:
Amps:
Amps are the flow of electricity that is measured as electric current . You can see the amps as the flow of water through a pipe. The more water passes through the pipe, the stronger the current.
Volts:
Volts are used to determine how much force is needed to make electric current flow . According to the previous example, you could think of volts as the pressure imposed on the water in a pipe, which causes the force for the water to flow.
Watts (watts):
The amps multiplied by volts are the watts, which is the measure used to determine the amount of energy consumed by electrical equipment. The higher the wattage, the greater the power in watts. In terms of the example of water, watts referred to the amount of water that has been released.