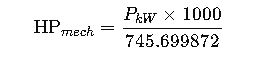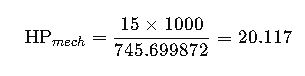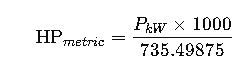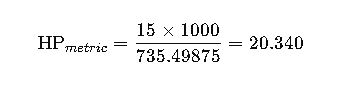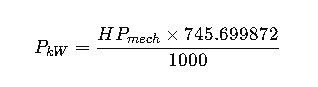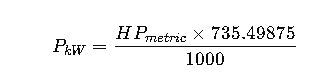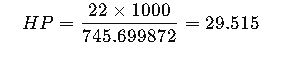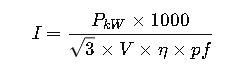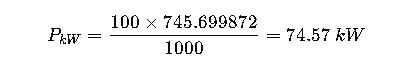Converting between kilowatts and horsepower is vital in engineering for motors, energy systems, and industrial design.
It requires understanding types of horsepower, efficiency, and standards like IEC and NEMA for accurate conversions.
kW to HP Converter
Extensive Conversion Table: Kilowatts to Horsepower (kW to HP)
The following tables present common kilowatt values converted to horsepower, using both metric horsepower (PS) and mechanical horsepower (HP). For clarity:
- 1 mechanical HP = 745.699872 W
- 1 metric HP (PS) = 735.49875 W
Table 1: Common kW to HP (Mechanical) Conversion Table
| Kilowatts (kW) | Horsepower (HP, mechanical) | Horsepower (HP, metric) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 0.335 | 0.340 |
| 0.37 | 0.496 | 0.503 |
| 0.55 | 0.738 | 0.748 |
| 0.75 | 1.006 | 1.020 |
| 1.1 | 1.475 | 1.496 |
| 1.5 | 2.012 | 2.040 |
| 2.2 | 2.951 | 2.993 |
| 3.0 | 4.022 | 4.078 |
| 4.0 | 5.364 | 5.437 |
| 5.5 | 7.376 | 7.500 |
| 7.5 | 10.059 | 10.170 |
| 11.0 | 14.749 | 14.782 |
| 15.0 | 20.117 | 20.340 |
| 18.5 | 24.816 | 25.167 |
| 22.0 | 29.515 | 29.994 |
| 30.0 | 40.235 | 40.680 |
| 37.0 | 49.675 | 50.171 |
| 45.0 | 60.352 | 61.020 |
| 55.0 | 73.812 | 74.460 |
| 75.0 | 100.587 | 101.700 |
| 90.0 | 120.704 | 122.040 |
| 110.0 | 147.190 | 149.820 |
| 132.0 | 176.583 | 179.520 |
| 160.0 | 214.688 | 217.920 |
| 200.0 | 268.360 | 272.160 |
| 250.0 | 335.450 | 340.200 |
| 315.0 | 422.358 | 428.580 |
Note: Always verify whether you’re using mechanical (US) or metric (EU/Asia) HP for your application.
Key Formulas for kW to HP Conversion
There are three main conversion formulas used depending on the type of horsepower you’re working with. These distinctions are crucial for ensuring accurate motor sizing or power rating in engineering contexts.
Formula 1: kW to Mechanical Horsepower (Imperial)
Where:

Example:
Formula 2: kW to Metric Horsepower (PS)
Where:
- 735.49875 = Watts per metric horsepower (PS, used in EU/Asia)
Example:
Formula 3: HP to kW Conversion
For reverse conversion:
- Mechanical HP:
- Metric HP:
Explanation of Variables and Typical Values

These constants are based on international metrology standards (see NIST reference).
Real-World Applications: Case Studies
Case Study 1: Industrial Motor Selection
Scenario:
An industrial facility in the U.S. is upgrading a conveyor system. The design requires a 22 kW motor, and the engineering team must ensure compatibility with the installed drives which are rated in HP.
Steps:
1.Convert 22 kW to HP (mechanical):
2.Round to standard motor sizes:
NEMA standard sizes include 30 HP motors, so a 30 HP motor would be chosen.
3.Check current draw:
Use the formula:

Result: 30 HP, 400V motor selected with 40 A full-load current.
Case Study 2: Electric Vehicle Motor Comparison
Scenario:
An engineer compares two EV motors—one rated at 75 kW and another at 100 HP—for torque analysis.
Steps:
1.Convert 100 HP (mechanical) to kW:
2.Compare Outputs:
- Motor A: 75 kW
- Motor B: 74.57 kW (100 HP)
3.Conclusion:
Power difference is negligible. Engineer chooses based on torque curve and weight efficiency.
Result: Conversion helped standardize comparison across metric and imperial units.
Factors That Influence Conversion Accuracy
While the formulas are fixed, real-world implementations vary depending on:
- Efficiency losses (e.g., motor ≠ 100% efficient)
- Voltage fluctuations
- Load types (inductive vs resistive)
- Ambient temperature and derating
Always validate nominal ratings with actual performance under load.
When to Use Mechanical vs Metric Horsepower
| Use Case | Recommended Unit |
|---|---|
| U.S. Industrial Equipment | Mechanical HP |
| EU/Asia Specifications | Metric HP (PS) |
| Automotive (International) | Usually Metric HP |
| Engineering Simulations | Typically use kW |
Regulatory and Engineering Standards
- IEC 60034 – Rotating electrical machines (kW as standard).
- NEMA MG1 – U.S. motors (HP used).
- ISO 1000 – SI units including kW.
More info:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is there a difference between electric and mechanical HP?
Yes. Electric HP (used in motors) is often rounded to 746 W, but true mechanical HP is defined as 745.699872 W. For precision, always use full value unless manufacturer uses nominal 746 W.
Why do some automotive systems report HP differently?
European vehicles use PS (Pferdestärke) which equals 735.49875 W. In North America, SAE-certified mechanical HP is standard.
Is the conversion reversible?
Yes. Conversions are symmetrical. However, due to rounding, reverse conversions may yield slightly different results (e.g., 75 kW → 100.587 HP → 75.01 kW). Use consistent precision.
Summary Table: All Conversions and Constants at a Glance
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| 1 HP (mechanical) | 745.699872 W |
| 1 HP (metric, PS) | 735.49875 W |
| 1 kW to HP (mechanical) | 1.341 |
| 1 kW to HP (metric) | 1.360 |
| 1 HP to kW (mechanical) | 0.7457 |
| 1 HP to kW (metric) | 0.7355 |