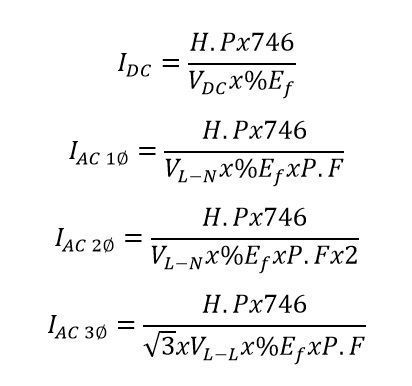Convert HP to Amps in seconds with our smart calculator, NEC tables, formulas, and examples.
Check single-phase, two-phase, and three-phase current based on voltage, efficiency, power factor, and frequency.
HP → Amps Calculator
Table of Hp to Amperes for 60 Hz AC Induction Motors
| Horsepower | Amperes Single-phase | Amperes Three-phase | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | — | ||||||
| 115V | 230V | 200V | 230V | 380-415V | 460V | 575V | |
| 1/6 | 4.4 | 2.2 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | |
| 1/4 | 5.8 | 2.9 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | |
| 1/3 | 7.2 | 3.6 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | |
| 1/2 | 9.8 | 4.9 | 2.5 | 2.2 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 0.9 |
| 3/4 | 13.8 | 6.9 | 3.7 | 3.2 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 1.3 |
| 1 | 16.0 | 8.0 | 4.8 | 4.2 | 2.3 | 2.1 | 1.7 |
| 1 1/2 | 20.0 | 10.0 | 6.9 | 6.0 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 2.4 |
| 2 | 24.0 | 12.0 | 7.8 | 6.8 | 4.3 | 3.4 | 2.7 |
| 3 | 34.0 | 17.0 | 11.0 | 9.6 | 6.1 | 4.8 | 3.9 |
| 5 | 56.0 | 28.0 | 17.5 | 15.2 | 9.7 | 7.6 | 6.1 |
| 7 1/2 | 80.0 | 40.0 | 25.0 | 22.0 | 14.0 | 11.0 | 9.0 |
| 10 | 100 | 50.0 | 32.0 | 28.0 | 18.0 | 14.0 | 11.0 |
| 15 | 135 | 68.0 | 48.0 | 42.0 | 27.0 | 21.0 | 17.0 |
| 20 | ~ | 88.0 | 62.0 | 54.0 | 34.0 | 27.0 | 22.0 |
| 25 | ~ | 110 | 78.0 | 68.0 | 43.0 | 34.0 | 27.0 |
| 30 | ~ | 136 | 92.0 | 80.0 | 51.0 | 40.0 | 32.0 |
| 40 | ~ | 176 | 120 | 104 | 66.0 | 52.0 | 41.0 |
| 50 | ~ | 216 | 150 | 130 | 83.0 | 65.0 | 52.0 |
| 60 | ~ | ~ | 177 | 154 | 103 | 77.0 | 62.0 |
| 75 | ~ | ~ | 221 | 192 | 128 | 96.0 | 77.0 |
| 100 | ~ | ~ | 285 | 248 | 165 | 124 | 99.0 |
| 125 | ~ | ~ | 359 | 312 | 208 | 156 | 125 |
| 150 | ~ | ~ | 414 | 360 | 240 | 180 | 144 |
| 175 | ~ | ~ | 475 | 413 | 275 | 207 | 168 |
| 200 | ~ | ~ | 552 | 480 | 320 | 240 | 192 |
| 250 | ~ | ~ | 692 | 602 | 403 | 302 | 242 |
| 300 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | 482 | 361 | 289 |
| 350 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | 560 | 414 | 336 |
| 400 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | 636 | 477 | 382 |
| 450 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | 711 | 515 | 412 |
| 500 | ~ | ~ | ~ | ~ | 786 | 590 | 472 |
The information in this chart was derived from NEC Tables 430-148 and 430-150, and Table 50.1 of the UL 508A standard. The voltages listed are nominal motor voltages. The listed currents are allowed for system voltage ranges of 110-120, 220-240, 380-415, 440-480, and 550-600 volts.
The full-load current values are for motors operating at standard speeds and with normal torque characteristics. Motors specifically designed for low speeds or high torques may have higher full-load currents, and multi-speed motors will have full-load currents that vary with speed. In these cases, the nameplate current ratings should be used.
Caution: Actual motor amperes may be higher or lower than the average values listed above. For more reliable motor protection, use the actual motor current as indicated on the motor nameplate. Use this table as a guide only.
Table of Motor Full-Load Currents from Hp to Amperes in DC
| Horsepower | 90V | 110-120V | 180V | 220-240V | 500V | 550-600V | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/10 | ~ | 2.0 | ~ | 1.0 | ~ | ~ | ||||||
| 1/8 | ~ | 2.2 | ~ | 1.1 | ~ | ~ | ||||||
| 1/6 1/4a | ~ 4.0 | 2.4 3.1 | ~ 2.0 | 1.2 1.6 | ~ ~ | ~ ~ | ||||||
| 1/3 | 5.2 | 4.1 | 2.6 | 2.0 | ~ | ~ | ||||||
| 1/2 | 6.8 | 5.4 | 3.4 | 2.7 | ~ | ~ | ||||||
| 3/4 | 9.6 | 7.6 | 4.8 | 3.8 | ~ | 1.6 | ||||||
| 1 | 12.2 | 9.5 | 6.1 | 4.7 | ~ | 2.0 | ||||||
| 1-1/2 | ~ | 13.2 | 8.3 | 6.6 | ~ | 2.7 | ||||||
| 2 | ~ | 17 | 10.8 | 8.5 | ~ | 3.6 | ||||||
| 3 | ~ | 25 | 16 | 12.2 | ~ | 5.2 | ||||||
| 5 | ~ | 40 | 27 | 20 | ~ | 8.3 | ||||||
| 7-1/2 | ~ | 58 | ~ | 29 | 13.6 | 12.2 | ||||||
| 10 | ~ | 76 | ~ | 38 | 18 | 16 | ||||||
| 15 | ~ | 110 | ~ | 55 | 27 | 24 | ||||||
| 20 | ~ | 148 | ~ | 72 | 34 | 31 | ||||||
Fundamental Formulas for HP to Amps Conversion
Converting horsepower to amperes requires understanding the relationship between mechanical power and electrical current. The formulas vary depending on whether the motor is single-phase or three-phase.
Single-Phase Motor Current Calculation
The current drawn by a single-phase motor can be calculated using the formula:
- I = Current in amperes (A)
- HP = Horsepower rating of the motor
- 746 = Conversion factor from HP to watts (1 HP = 746 W)
- V = Voltage supply in volts (V)
- η = Motor efficiency (decimal form, e.g., 0.9 for 90%)
- PF = Power factor (decimal form, e.g., 0.85)
This formula calculates the input current by dividing the mechanical power converted to electrical power by the product of voltage, efficiency, and power factor.
Three-Phase Motor Current Calculation
For three-phase motors, the current is calculated differently due to the nature of three-phase power:
- I = Current in amperes (A)
- HP = Horsepower rating of the motor
- 746 = Conversion factor from HP to watts
- √3 ≈ 1.732, accounts for three-phase power
- V = Line-to-line voltage in volts (V)
- η = Motor efficiency (decimal)
- PF = Power factor (decimal)
The √3 factor arises from the vector sum of the three-phase currents and voltages, which affects the total current calculation.
Explanation of Variables and Typical Values
- Horsepower (HP): Mechanical power output of the motor. Common values range from fractional HP (0.5 HP) to large industrial motors (100+ HP).
- Voltage (V): The supply voltage, which can be single-phase (120V, 240V) or three-phase (208V, 230V, 460V, 575V).
- Efficiency (η): Ratio of mechanical output power to electrical input power. Typical motor efficiencies range from 85% to 96% depending on motor class and size.
- Power Factor (PF): Ratio of real power to apparent power, typically between 0.8 and 0.95 for motors under full load.
Real-World Applications of HP to Amps Conversion
Accurate HP to Amps calculations are critical in designing electrical systems, selecting circuit breakers, and ensuring motor protection. Below are two detailed examples illustrating practical applications.
Example 1: Single-Phase Motor Current Calculation
A 3 HP single-phase motor operates on a 240 V supply. The motor has an efficiency of 87% and a power factor of 0.9. Calculate the full load current.
Step 1: Identify variables:
- HP = 3
- V = 240 V
- η = 0.87
- PF = 0.9
Step 2: Apply the single-phase formula:
Step 3: Calculate numerator:
- 3 × 746 = 2238 W
Step 4: Calculate denominator:
- 240 × 0.87 × 0.9 = 188.16
Step 5: Calculate current:
- I = 2238 / 188.16 ≈ 11.89 A
The motor will draw approximately 11.9 amps at full load.
Example 2: Three-Phase Motor Current Calculation
A 10 HP three-phase motor runs on a 460 V supply with 92% efficiency and a power factor of 0.88. Determine the full load current.
Step 1: Identify variables:
- HP = 10
- V = 460 V
- η = 0.92
- PF = 0.88
Step 2: Apply the three-phase formula:
Step 3: Calculate numerator:
- 10 × 746 = 7460 W
Step 4: Calculate denominator:
- 1.732 × 460 × 0.92 × 0.88 ≈ 661.5
Step 5: Calculate current:
- I = 7460 / 661.5 ≈ 11.28 A
The motor draws approximately 11.3 amps at full load.
Additional Considerations for Accurate HP to Amps Calculations
While the formulas and tables provide a solid foundation, several factors can influence the actual current drawn by a motor:
- Starting Current: Motors typically draw 5 to 7 times their full load current during startup, which must be considered for circuit protection.
- Load Variations: Partial loads reduce current draw, but power factor and efficiency may also change.
- Temperature Effects: Higher ambient temperatures can affect motor efficiency and current.
- Voltage Fluctuations: Variations in supply voltage impact current and motor performance.
For precise motor sizing and protection, always refer to manufacturer datasheets and applicable electrical codes such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) or IEC standards.
Summary of Key Points for HP to Amps Conversion
- Horsepower to amps conversion depends on motor type (single or three-phase), voltage, efficiency, and power factor.
- Use the formula I = (HP × 746) / (V × η × PF) for single-phase motors.
- Use the formula I = (HP × 746) / (√3 × V × η × PF) for three-phase motors.
- Consult tables for quick reference of common motor ratings and their typical current draws.
- Consider real-world factors such as starting current and load variations for accurate electrical design.
Recommended External Resources for Further Reading
Eaton – Motor Protection and Sizing
National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) – Standards and motor data
National Electrical Code (NEC) – Electrical installation guidelines