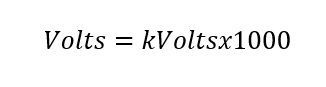With this online calculator (online) you can convert from kilovolt to volt automatically, easily, quickly and for free.
We also explain how to convert from kvolts to volts in 1 single step, which formula is used for the calculation and a table with the main conversions from kv to volts.
Formula to convert, calculate and transform from kilovolts to volts , single-phase, two-phase and three-phase:
- kVolts = kilovolts.
- Volts = Voltage.
How to convert from kVolts to volts in only 1 steps:
Step 1:
Multiply kvolts by 1000, for example, if an engine is 10 kV, you must multiply 10kVx1000 which will result in 10000Volt.
Table kilovolts to volts, conversion, equivalence, transformation :
Definitions kvoltios and Voltios:
V (Volts) = The volt (symbolized by the letter V) is the international standard unit (SI) of electric potential or electromotive force.
A potential of one volt appears through a resistance of one ohm when a current of one ampere flows through that resistance.
The voltage can be expressed as an average value in a given time interval, as an instantaneous value at a specific moment in time, or as an effective or quadratic mean value (rms). The average and instantaneous voltages receive a negative (-) or positive (+) polarity with respect to a zero or terrestrial reference potential. The rms voltage is a dimensionless quantity, always represented by a non-negative real number.
For a stable source of electric direct current (DC) potential, such as that of an alkaline or carbon-zinc electrochemical cell, the average and instantaneous voltages are both approximately +1.5 V if the negative terminal is considered common ground; the rms voltage is 1.5 V. For the standard service alternating current (AC), the average voltage is zero (the polarity is constantly reversed);the instantaneous voltage ranges from approximately -165 V to +165 V; The effective voltage is nominally 117 V.
Voltages are sometimes expressed in units that represent power multiples of 10 or fractions of a volt.
kV (kilovolts) = One kilovolt (kV symbolized) is equal to one thousand volts (1 kV = 1000 V).