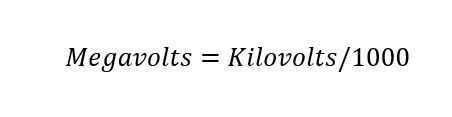This calculator is an online tool (online) with which you can convert from kilovolt to Megavolt automatically, easily, quickly and for free.
We also explain how to convert kvolts to megavolts in 1 single step, with the help of the formula used for the calculation and with the table that has the main conversions from kv to megavolts.
Formula from conversion, calculate and transform from kilovolts to megavolts, single-phase, two-phase and three-phase:
kVolts=1000 volts.
MegaVolts= 1000 kVolts
How to convert or switch from kVolts to megavolts in only 1 steps:
Step 1:
Divide kV by 1000, for example, if a compressor has a voltage of 20 kV, it should be divided by 20kV / 1000 which will result in 0.02Megavolt.
Table kv to megavolts, conversion, equivalence, transformation:
| kVolts | Megavolts |
| How many 1 kVolts | 0,001 Megavolts |
| How many 2 kVolts | 0,002 Megavolts |
| How many 3 kVolts | 0,003 Megavolts |
| How many 4 kVolts | 0,004 Megavolts |
| How many 5 kVolts | 0,005 Megavolts |
| How many 6 kVolts | 0,006 Megavolts |
| How many 7 kVolts | 0,007 Megavolts |
| How many 8 kVolts | 0,008 Megavolts |
| How many 9 kVolts | 0,009 Megavolts |
| How many 10 kVolts | 0,01 Megavolts |
| How many 20 kVolts | 0,02 Megavolts |
| How many 30 kVolts | 0,03 Megavolts |
| How many 40 kVolts | 0,04 Megavolts |
| How many 50 kVolts | 0,05 Megavolts |
| How many 60 kVolts | 0,06 Megavolts |
| How many 70 kVolts | 0,07 Megavolts |
| How many 80 kVolts | 0,08 Megavolts |
| How many 90 kVolts | 0,09 Megavolts |
| How many 100 kVolts | 0,1 Megavolts |
| How many 200 kVolts | 0,2 Megavolts |
| How many 300 kVolts | 0,3 Megavolts |
| How many 400 kVolts | 0,4 Megavolts |
| How many 500 kVolts | 0,5 Megavolts |
| How many 600 kVolts | 0,6 Megavolts |
| How many 700 kVolts | 0,7 Megavolts |
| How many 800 kVolts | 0,8 Megavolts |
| How many 900 kVolts | 0,9 Megavolts |
| How many 1000 kVolts | 1 Megavolts |
Definitions kvoltios and Megavolts:
V (Volts) = The volt (symbolized by the letter V) is the international standard unit (SI) of electric potential or electromotive force.
A potential of one volt appears through a resistance of one ohm when a current of one ampere flows through that resistance.
The voltage can be expressed as an average value in a given time interval, as an instantaneous value at a specific moment in time, or as an effective or quadratic mean value (rms). The average and instantaneous voltages receive a negative (-) or positive (+) polarity with respect to a zero or terrestrial reference potential. The rms voltage is a dimensionless quantity, always represented by a non-negative real number.
For a stable source of electric direct current (DC) potential, such as that of an alkaline or carbon-zinc electrochemical cell, the average and instantaneous voltages are both approximately +1.5 V if the negative terminal is considered common ground; the rms voltage is 1.5 V. For the standard service alternating current (AC), the average voltage is zero (the polarity is constantly reversed); the instantaneous voltage ranges from approximately -165 V to +165 V; The effective voltage is nominally 117 V.
Voltages are sometimes expressed in units that represent power multiples of 10 or fractions of a volt.
Megavolts = One megavolt (MV symbolized) is equal to one kvolts divided by 1000 (1 MV = 1kV / 1000).