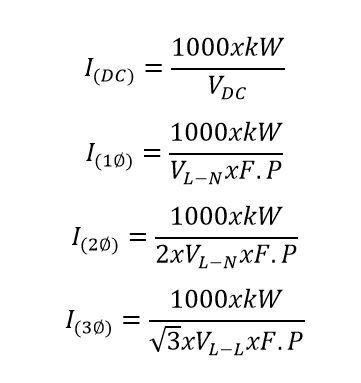The conversion of Volts to Amperes is very simple and you can do it with this tool.
We explain that formula is used in the calculation, also how to convert from Volts to Amperes in only 3 steps , we show some examples and a table with the main conversions from volts to Amperes.
To facilitate the calculations we show the most common power factors of different constructions, appliances and motors.
Formula to convert, pass, calculate and transform from Volts to Amperes, single-phase, two-phase and three-phase:
- kW = kilowatt or kilowatts.
- V L-N = Volts line to neutral.
- V L-L = Volts line to line.
- I AC1Ø = Current / Amps 1 phase.
- I AC2Ø = Current / Amps 2 phase.
- I AC3Ø = Current / Amps 3 phase.
- I DC = Direct current.
- FP = Power factor.
How to convert from Volts to Amperes in only 3 steps:
To change from volts to amperes, you only have to multiply and divide the variables shown in the formula, according to the type of DC or AC current and the number of phases.
Step 1:
Multiply the kW by 1000. For example, if you have a drill that consumes 0.9kW, you must multiply 0.9 × 1000, getting 900, (0.9 × 1000) = 900.
Step 2:
Multiply the corresponding voltage according to the formula by the power factor and by the root of three, as long as the equipment is three-phase. For example, if I have a three-phase 480V drill with a power factor of 0.87, I multiply 480 × 0.87x√3 and get 723.3 ((480 × 0.87x√3) = 723.3.) .
Divide step 1 between step 2. (0.9 × 1000) / (480 × 0.87x√3) and get 1.24A.
Examples of conversions from Volts to Amperes:
Example 1:
A single-phase LED luminaire – alternating current (AC) of 0.33kW, with a neutral line voltage of 127V and line line of 208V, a power factor of 0.93, how many monophasic amperes does the LED luminaire have ?.
Answer: // To know the answer you must multiply the kW by 1000 (0.33kWx1000), and then divide the result between the voltage by the power factor as indicated by the formula in single-phase systems: 0.33kWx1000 / 127 × 0, 93 = 2.54A.
Example 2:
A three phase blender (AC) consumes 4.7kW, has a linear line voltage of 460V and a power factor of 0.87, how can I convert from Volts to three phase amps ?.
Answer: // Initially what you must do is multiply the power in kW by 1000 (4.7kWx1000), which will result in 4700, then you must divide this result between the multiplication of the voltage by the power factor and root of three, as follows: 460Vx0.87x√3 = 693.1, finally divide 4700 / 693.1 = 6.78A.
Example 3:
There is a UPS with a power of 2.9kW bifasic (AC), a line-to-line voltage of 208V and a neutral line voltage of 120V, with a power factor of 0.95, which amperage has the UPS ?.
Answer: // You must multiply the kW per thousand, in the following way: 2.9kWx1000 and then divide the above between the multiplication of the voltage, the power factor and two, as indicated by the biphasic formula, being as follows : (2,9kWx1000) / (2x120x0,95), which will result in: 12.72A.
Table of Volts to three-phase amperes, conversion, equivalence, transformation (kW = 5, Fp = 0.8, AC, 3F):
Note : The changes of Volts to amperes of the previous table were made taking into account a power factor of 0.8, a power of 5kW AC three phase. For different variables you should use the calculator that appears at the beginning.
How to use the Calculator from Volts to Amperes:
The first thing you must do is enter the Volts you want to convert, then choose the AC or DC current, it is important that once you choose the current you review the data shown on the left of the table, these change according to the current type chosen, then choose the number of phases: 1,2 or 3, this option will only be available if AC current is chosen.
Then enter the power , finally the power factor and then click on calculate to finish or restart to enter new values.
Typical power factor for engines, constructions and appliances.
Typical Un-improved Power Factor by Industry:
Typical power factor of common household electronics:
| Electronics device | Power Factor |
| Magnavox Projection TV – standby | 0,37 |
| Samsung 70″ 3D Bluray | 0,48 |
| Digital Picture Frame | 0,52 |
| ViewSonic Monitor | 0,5 |
| Dell Monitor | 0,55 |
| Magnavox Projection TV | 0,58 |
| Digital Picture Frame | 0,6 |
| Digital Picture Frame | 0,62 |
| Digital Picture Frame | 0,65 |
| Philips 52″ Projection TV | 0,65 |
| Wii | 0,7 |
| Digital Picture Frame | 0,73 |
| Xbox Kinect | 0,75 |
| Xbox 360 | 0,78 |
| Microwave | 0,9 |
| Sharp Aquos 3D TV | 0,95 |
| PS3 Move | 0,98 |
| Playstation 3 | 0,99 |
| Element 41″ Plasma TV | 0,99 |
| Current large, flat-screen television | 0,96 |
| Windows-mount air conditioner | 0,9 |
| Legacy CRT-Based color television | 0,7 |
| Legacy flat panel computer monitor | 0,64 |
| While-LED lighting fixture | 0,61 |
| Legacy laptop power adapter | 0,55 |
| Laser Printer | 0,5 |
| Incandescent lamps | 1 |
| Fluorescent lamps (uncompensated) | 0,5 |
| Fluorescent lamps (compensated) | 0,93 |
| Discharge lamps | 0,4-0,6 |
Typical Motor Power Factors:
| Power | Speed | Power Factor | ||
| (hp) | (rpm) | 1/2 load | 3/4 load | full load |
| 0 – 5 | 1800 | 0.72 | 0.82 | 0.84 |
| 5 – 20 | 1800 | 0.74 | 0.84 | 0.86 |
| 20 – 100 | 1800 | 0.79 | 0.86 | 0.89 |
| 100 – 300 | 1800 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 0.91 |
Reference // Power Factor in Electrical Energy Management-A. Bhatia, B.E.-2012
Power Factor Requirements for Electronic Loads in California- Brian Fortenbery,2014
http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com
Qualify Calculator from Volts to Amperes: [kkstarratings]