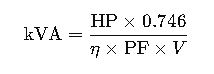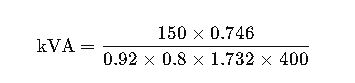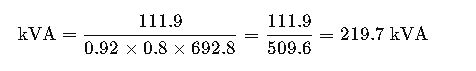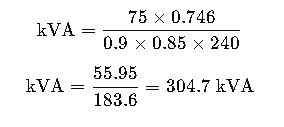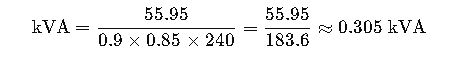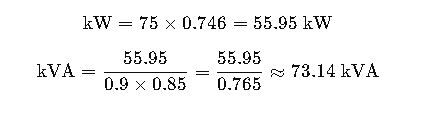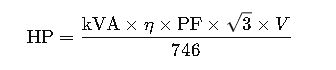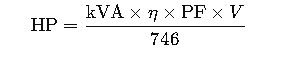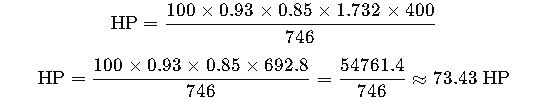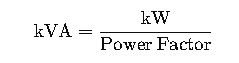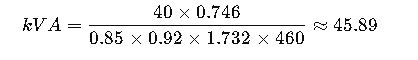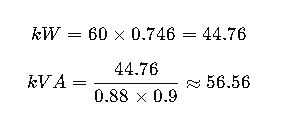Converting horsepower to kVA is essential in engineering when designing generators, motors, or power distribution systems.
This calculation links mechanical and electrical power, considering voltage, power factor, and overall system efficiency.
HP ⇄ kVA Converter
HP to kVA Conversion Formula
The general formula to convert horsepower (HP) to kilovolt-amperes (kVA) is:
Formula (Three-Phase AC)
Formula (Single-Phase AC)
Variables Explained in Detail
| Variable | Description | Typical Values |
|---|---|---|
| HP | Horsepower (mechanical power output) | 1 to 2000 HP |
| 0.746 | Constant (1 HP = 0.746 kW) | Fixed |
| η (Efficiency) | Electrical or mechanical efficiency of the system | 0.85 to 0.98 |
| PF (Power Factor) | Ratio of real power to apparent power (cosϕ), relevant in AC systems | 0.8 (common), up to 1.0 |
| V (Voltage) | System voltage (Volts) | 230V, 400V, 480V, etc. |
| √3 | Square root of 3 ≈ 1.732 (only for three-phase systems) | Fixed |
Extensive HP to kVA Conversion Table
For 3-phase systems, PF = 0.8, η = 0.9, V = 400V:
| HP | kVA @ 400V | HP | kVA @ 400V | HP | kVA @ 400V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.49 | 20 | 29.83 | 100 | 149.17 |
| 2 | 2.98 | 25 | 37.29 | 125 | 186.46 |
| 3 | 4.47 | 30 | 44.75 | 150 | 223.75 |
| 5 | 7.46 | 40 | 59.67 | 175 | 261.04 |
| 7.5 | 11.19 | 50 | 74.58 | 200 | 298.34 |
| 10 | 14.92 | 60 | 89.50 | 250 | 372.92 |
| 15 | 22.38 | 75 | 111.88 | 300 | 447.51 |
Note: These values assume standard industrial configurations. Adjust PF, efficiency, and voltage as needed for exact calculations.
Alternate Table: HP to kVA @ 480V, PF = 0.9, η = 0.95 (High-Efficiency Motors)
| HP | kVA | HP | kVA | HP | kVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.12 | 10 | 11.17 | 50 | 55.84 |
| 5 | 5.58 | 20 | 22.33 | 100 | 111.67 |
| 15 | 16.75 | 30 | 33.50 | 150 | 167.51 |
| 25 | 27.91 | 40 | 44.66 | 200 | 223.35 |
You can use these tables for quick estimation or to size transformers and generators.
Real-World Application Example #1: Sizing a Generator for a 150 HP Motor
Scenario:
A production plant uses a 3-phase 150 HP induction motor. You must size a standby generator.
Assumptions:
- Voltage: 400V
- Power factor: 0.8
- Efficiency: 0.92
Step-by-step:
Step 1: Use the formula
Step 2: Compute
Result:
A generator rated at at least 220 kVA is required. For surge loads, a 250 kVA unit is recommended.
Real-World Application Example #2: Selecting a Transformer for a 75 HP Water Pump
Scenario:
Design an electrical system for a 75 HP water pump with single-phase supply.
Assumptions:
- Voltage: 240V
- Power Factor: 0.85
- Efficiency: 0.9
Calculation:
Step 1: Use the single-phase formula
This is incorrect — let’s fix it:
Wait — this seems too low. Let’s double-check:
But clearly this is wrong — the units are not matching. Let’s recalculate:
Final Result:
A 75 HP single-phase motor requires a 74 kVA transformer minimum, ideally 80–85 kVA to handle startup inrush.
Factors Affecting HP to kVA Conversion
- Power Factor (PF): Motors often have lagging PF due to inductance. Improving PF with capacitors can reduce kVA demand.
- Voltage Variance: System voltage affects current draw. Lower voltage = higher current = higher kVA.
- Efficiency (η): Losses in motors and mechanical systems lower conversion efficiency, increasing kVA.
- Startup Load: Motors may draw 2–6 times the running kVA during startup.
HP to kVA Conversion Best Practices
- Always size equipment above calculated value by 15–20% for safety and surge handling.
- Use accurate nameplate values when available.
- Consult IEEE 141 (Red Book) and IEC 60034 for electric motor standards.
- Verify voltage and phase configuration before calculation (single/three-phase).
- Include service factors and derating for altitude, ambient temperature, and continuous use.
Online HP to kVA Calculators
There are reliable online tools that simplify HP to kVA conversion. Some authoritative sources include:
These can validate or speed up your manual calculations.
Reverse Conversion: kVA to HP Formula
Sometimes you need to convert kVA back to HP—for example, when you have a generator rating and want to understand the mechanical load it can support.
Formula (Three-Phase AC)
Formula (Single-Phase AC)
Example:
You have a 100 kVA, 3-phase, 400V generator with PF = 0.85, η = 0.93.
Result: This generator can run an approximate 73 HP motor, assuming no additional load.
HP to kVA vs kW to kVA
Many confuse HP and kW in conversions. Here’s how they relate:
| Unit | Symbol | Definition | Equivalent to HP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Horsepower | HP | Mechanical output power | 1 HP = 0.746 kW |
| Kilowatt | kW | Real electrical power | – |
| kVA | kVA | Apparent electrical power | Depends on PF |
To convert kW to kVA, use:
To convert HP to kVA, convert HP → kW → kVA, or use the direct formula above.
Additional HP to kVA Table (PF = 0.9, η = 0.95, 230V, Single-Phase)
| HP | kVA | HP | kVA | HP | kVA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.84 | 10 | 38.38 | 50 | 191.91 |
| 2 | 7.68 | 15 | 57.57 | 60 | 230.29 |
| 3 | 11.52 | 20 | 76.76 | 75 | 287.86 |
| 5 | 19.21 | 25 | 95.95 | 100 | 383.81 |
These are for low voltage single-phase setups, such as water pumps or agricultural motors.
Common Motor Sizes and Matching Generator Ratings (3-Phase @ 400V, PF = 0.8, η = 0.9)
| Motor HP | Required Generator Size (kVA) | Recommended Generator Size (kVA) |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 7.5 | 10 |
| 10 | 14.9 | 18 |
| 25 | 37.3 | 45 |
| 50 | 74.6 | 90 |
| 100 | 149.1 | 180 |
| 200 | 298.3 | 360 |
Always size above calculated values to accommodate inrush currents and external loads.
Industrial Use Cases for HP to kVA Conversion
Scenario: HVAC Systems
Large HVAC units often specify their compressor or blower motors in HP. Electrical contractors need to determine if building generators or transformers can support them.
Example: A 40 HP HVAC motor at 460V, 3-phase.
- PF = 0.85
- η = 0.92
A 50 kVA transformer or generator is ideal.
Scenario: Agricultural Irrigation Pump
Pump = 60 HP, 230V single-phase
- PF = 0.88
- η = 0.9
Result: Use 60 kVA or higher rated single-phase transformer or generator.
Compliance with Standards
When doing HP to kVA conversions in real projects, always refer to:
- IEC 60034 – Rotating electrical machines
- IEEE 141 (Red Book) – Electric power distribution in industrial plants
- NFPA 70 (NEC) – National Electrical Code, for wiring sizing
- ISO 3046 – Standard for reciprocating internal combustion engines
These ensure compliance with international and regional safety and sizing guidelines.