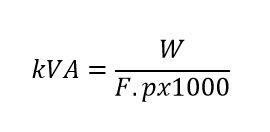To convert from watts to kVA you just have to divide the watts by the power factor x 1000, this is the base formula of the calculator.
We also show some descriptive examples , the main steps for the conversion and the main equivalences in a table . If you do not know the power factor of the load.
Definition F.P, S (kva) and P (Watts):
Watts: is Working Power (also called Actual Power or Active Power or Real Power). It is the power that actually powers the equipment and performs useful work.
The real power in watts is the power that performs work or generates heat. Power in watts is the rate at which energy is consumed (or generated). One watt is one joule (energy) per second (1 W = 1 J/s).
Resistive devices or loads such as heaters, incandescent lamps are rated in Watts.
kVA: A kilovolt-ampere, commonly referred to as a kVA, is commonly used as a unit of power in obtaining the electrical capacity of circuit breakers, uninterrupted power supplies and wirings.
KVA is larger than KW because loads are inductive such as motors, discharge lighting, reactors and more current is required to keep the magnetic field energized than is -turned into heat (KW).
Inductive devices or loads such,. as tansformers and motors having power factor less than 1.0 are generally rated in KVA.
F.p: Power factor is the ratio of working power to apparent power. It measures how effectively electrical power is being used. A high power factor signals efficient utilization of electrical power, while a low power factor indicates poor utilization of electrical power.
Power Factor is the cosine of the phase angle between current and voltage.
Power Factor is the ratio of true power to apparent power.
Watts to kVA calculation formula:
Typical Un-improved Power Factor by Industry:
Typical power factor of common household electronics:
Typical Motor Power Factors:
| Power | Speed | Power Factor | ||
| (hp) | (rpm) | 1/2 load | 3/4 load | full load |
| 0 – 5 | 1800 | 0.72 | 0.82 | 0.84 |
| 5 – 20 | 1800 | 0.74 | 0.84 | 0.86 |
| 20 – 100 | 1800 | 0.79 | 0.86 | 0.89 |
| 100 – 300 | 1800 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 0.91 |
Reference // Power Factor in Electrical Energy Management-A. Bhatia, B.E.-2012
Power Factor Requirements for Electronic Loads in California- Brian Fortenbery,2014
http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com
Watts to kVA conversion table-chart:
| Watts | f.p | kVA |
| 1 | 0,8 | 0,001 |
| 2 | 0,8 | 0,003 |
| 3 | 0,8 | 0,004 |
| 4 | 0,8 | 0,005 |
| 5 | 0,8 | 0,006 |
| 6 | 0,8 | 0,008 |
| 7 | 0,8 | 0,009 |
| 8 | 0,8 | 0,010 |
| 9 | 0,8 | 0,011 |
| 10 | 0,8 | 0,013 |
| 20 | 0,85 | 0,024 |
| 30 | 0,85 | 0,035 |
| 40 | 0,85 | 0,047 |
| 50 | 0,85 | 0,059 |
| 60 | 0,85 | 0,071 |
| 70 | 0,85 | 0,082 |
| 80 | 0,85 | 0,094 |
| 90 | 0,85 | 0,106 |
| 100 | 0,85 | 0,118 |
| 200 | 0,9 | 0,222 |
| 300 | 0,9 | 0,333 |
| 400 | 0,9 | 0,444 |
| 500 | 0,9 | 0,556 |
| 600 | 0,9 | 0,667 |
| 700 | 0,9 | 0,778 |
| 800 | 0,9 | 0,889 |
| 900 | 0,9 | 1,000 |
| 1000 | 0,9 | 1,111 |
| 2000 | 0,95 | 2,105 |
| 3000 | 0,95 | 3,158 |
| 4000 | 0,95 | 4,211 |
| 5000 | 0,95 | 5,263 |
| 6000 | 0,95 | 6,316 |
| 7000 | 0,95 | 7,368 |
| 8000 | 0,95 | 8,421 |
| 9000 | 0,95 | 9,474 |
| 10000 | 1 | 10,000 |
| 20000 | 1 | 20,000 |
| 30000 | 1 | 30,000 |
| 40000 | 1 | 40,000 |
| 50000 | 1 | 50,000 |
| 60000 | 1 | 60,000 |
| 70000 | 1 | 70,000 |
| 80000 | 1 | 80,000 |
| 90000 | 1 | 90,000 |
| 100000 | 1 | 100,000 |