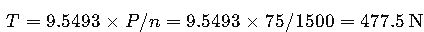Comprehensive engineer-level guide covering torsional design of solid and hollow shafts, including tables of diameters. Includes polar inertia, twist, formulas for stress, stiffness, torque, material properties, safety factors, fatigue, examples.
Torque Calculator — Solid & Hollow Shafts
Quick Reference Tables — Common Shaft Sizes (Metric)
The following tables provide values of polar moment of inertia J, polar section modulus Zp, shear stress for a reference torque T=1000 N⋅m, and elastic twist in degrees per metre (assuming steel with shear modulus G=79 GPa).
These are highly practical for engineers who need to quickly size shafts or check preliminary designs.
Solid Circular Shafts (d = 10 mm → 200 mm, step 10 mm)
| d (mm) | d (in) | J (m⁴) | J (mm⁴) | Zp (m³) | Zp (mm³) | τ @1000 N·m (MPa) | Twist deg/m @1000 N·m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.394 | 9.817e-10 | 9.817e+02 | 1.963e-07 | 1.963e+02 | 5092.958 | 738.747 |
| 20 | 0.787 | 1.571e-08 | 1.571e+04 | 1.571e-06 | 1.571e+03 | 636.620 | 46.172 |
| 30 | 1.181 | 7.952e-08 | 7.952e+04 | 5.301e-06 | 5.301e+03 | 188.653 | 9.764 |
| 40 | 1.575 | 2.0106e-07 | 2.0106e+05 | 1.005e-05 | 1.005e+04 | 99.735 | 3.858 |
| 50 | 1.969 | 4.909e-07 | 4.909e+05 | 1.964e-05 | 1.964e+04 | 50.940 | 1.505 |
| 60 | 2.362 | 1.273e-06 | 1.273e+06 | 3.244e-05 | 3.244e+04 | 30.803 | 0.672 |
| 70 | 2.756 | 2.672e-06 | 2.672e+06 | 7.634e-05 | 7.634e+04 | 13.092 | 0.339 |
| 80 | 3.150 | 4.021e-06 | 4.021e+06 | 1.005e-04 | 1.005e+05 | 9.950 | 0.188 |
| 90 | 3.543 | 6.106e-06 | 6.106e+06 | 1.357e-04 | 1.357e+05 | 7.367 | 0.111 |
| 100 | 3.937 | 9.817e-06 | 9.817e+06 | 1.963e-04 | 1.963e+05 | 5.093 | 0.074 |
| 110 | 4.331 | 1.437e-05 | 1.437e+07 | 2.613e-04 | 2.613e+05 | 3.826 | 0.052 |
| 120 | 4.724 | 2.043e-05 | 2.043e+07 | 3.405e-04 | 3.405e+05 | 2.936 | 0.037 |
| 130 | 5.118 | 2.787e-05 | 2.787e+07 | 4.289e-04 | 4.289e+05 | 2.334 | 0.027 |
| 140 | 5.512 | 3.673e-05 | 3.673e+07 | 5.247e-04 | 5.247e+05 | 1.853 | 0.020 |
| 150 | 5.906 | 4.704e-05 | 4.704e+07 | 6.272e-04 | 6.272e+05 | 1.452 | 0.015 |
| 160 | 6.299 | 5.884e-05 | 5.884e+07 | 7.355e-04 | 7.355e+05 | 1.180 | 0.012 |
| 170 | 6.693 | 7.217e-05 | 7.217e+07 | 8.492e-04 | 8.492e+05 | 0.999 | 0.009 |
| 180 | 7.087 | 8.704e-05 | 8.704e+07 | 9.671e-04 | 9.671e+05 | 0.821 | 0.007 |
| 190 | 7.480 | 1.035e-04 | 1.035e+08 | 1.090e-03 | 1.090e+06 | 0.729 | 0.006 |
| 200 | 7.874 | 1.274e-04 | 1.274e+08 | 1.274e-03 | 1.274e+06 | 0.624 | 0.005 |
Hollow Shafts (outer diameter do, inner diameter di = 0.60·do)
| do (mm) | do (in) | di (mm) | J (m⁴) | J (mm⁴) | Zp (m³) | τ @1000 N·m (MPa) | Twist deg/m @1000 N·m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.394 | 6.0 | 3.230e-10 | 3.230e+02 | 6.460e-08 | 15479.197 | 2250.168 |
| 20 | 0.787 | 12.0 | 1.367e-08 | 1.367e+04 | 1.367e-06 | 731.411 | 53.047 |
| 30 | 1.181 | 18.0 | 6.922e-08 | 6.922e+04 | 4.614e-06 | 216.714 | 10.478 |
| 40 | 1.575 | 24.0 | 1.750e-07 | 1.750e+05 | 8.748e-06 | 114.275 | 4.429 |
| 50 | 1.969 | 30.0 | 4.337e-07 | 4.337e+05 | 1.734e-05 | 57.723 | 1.784 |
| 60 | 2.362 | 36.0 | 1.124e-06 | 1.124e+06 | 3.747e-05 | 26.688 | 0.799 |
| 70 | 2.756 | 42.0 | 2.283e-06 | 2.283e+06 | 6.524e-05 | 15.334 | 0.401 |
| 80 | 3.150 | 48.0 | 3.439e-06 | 3.439e+06 | 8.598e-05 | 11.628 | 0.234 |
| 90 | 3.543 | 54.0 | 5.076e-06 | 5.076e+06 | 1.128e-04 | 8.846 | 0.139 |
| 100 | 3.937 | 60.0 | 7.244e-06 | 7.244e+06 | 1.449e-04 | 6.900 | 0.092 |
| 110 | 4.331 | 66.0 | 1.014e-05 | 1.014e+07 | 1.847e-04 | 5.412 | 0.063 |
| 120 | 4.724 | 72.0 | 1.367e-05 | 1.367e+07 | 2.275e-04 | 4.396 | 0.048 |
| 130 | 5.118 | 78.0 | 1.833e-05 | 1.833e+07 | 2.821e-04 | 3.546 | 0.037 |
| 140 | 5.512 | 84.0 | 2.413e-05 | 2.413e+07 | 3.447e-04 | 2.901 | 0.029 |
| 150 | 5.906 | 90.0 | 3.107e-05 | 3.107e+07 | 4.143e-04 | 2.412 | 0.023 |
| 160 | 6.299 | 96.0 | 3.914e-05 | 3.914e+07 | 4.892e-04 | 2.020 | 0.018 |
| 170 | 6.693 | 102.0 | 4.833e-05 | 4.833e+07 | 5.669e-04 | 1.813 | 0.015 |
| 180 | 7.087 | 108.0 | 5.864e-05 | 5.864e+07 | 6.516e-04 | 1.534 | 0.012 |
| 190 | 7.480 | 114.0 | 7.007e-05 | 7.007e+07 | 7.373e-04 | 1.356 | 0.010 |
| 200 | 7.874 | 120.0 | 8.263e-05 | 8.263e+07 | 8.263e-04 | 1.210 | 0.008 |
Fundamental Formulas for Torque Calculation

Typical Values for Design
- Shear modulus GGG:
- Steel: ~79 GPa
- Aluminum: ~26 GPa
- Yield strength (σy):
- Mild steel (A36): 250 MPa
- Stainless steel (304 annealed): 205 MPa
- Alloy steels: 400–1200 MPa
- Factor of safety (FS):
- Static loading: 1.5–3
- Fatigue-critical: 2–5+
- Keyway stress concentration factor (Kt): 1.5–2.0 typical.
Worked Example 1 — Solid Shaft
Problem:
Transmit 75 kW at 1500 rpm using solid steel shaft (σy = 250 MPa). FS = 2.
Answer:
Use 35 mm stock shaft.
Worked Example 2 — Hollow Shaft
Problem:
Transmit 5000 N·m with max twist ≤ 0.5°/m. Steel (G = 79 GPa), di/do = 0.6.
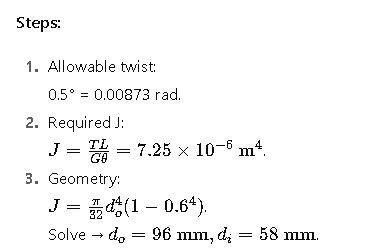
Answer:
Hollow shaft 96 mm OD, 58 mm ID.
Advanced Design Considerations
- Always check fatigue if shaft rotates continuously.
- Include surface finish, size, and reliability factors.
- Consider bending + torsion combined stresses.
- Perform FEA for complex geometries.
- Verify critical speeds for long/high-speed shafts.
Professional Design Checklist
- Verify certified material properties (σy, G).
- Select nearest standard shaft diameter.
- Apply stress concentration factors (Kt).
- Perform fatigue analysis (S–N approach).
- Check torsional stiffness (θ per metre).
- Validate design with FEA.
- Check dynamic response (critical speed, torsional modes).