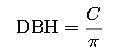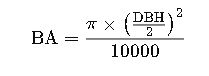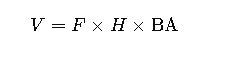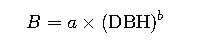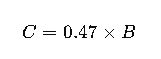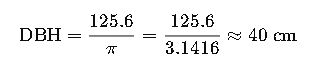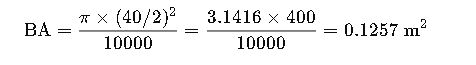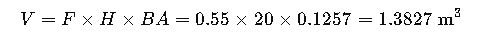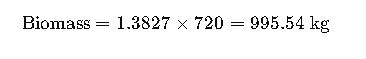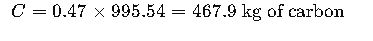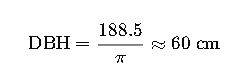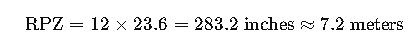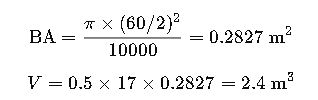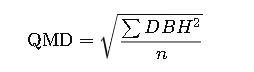Measuring diameter at breast height (DBH) is essential in forestry, ecology, carbon studies, and biomass evaluation.
DBH reveals tree growth, forest structure, and carbon potential. This guide offers formulas, tables, and examples.
Tree DBH Calculator
Common DBH Values for Different Tree Species
The following table provides typical DBH ranges for mature specimens of common tree species. These values are based on data from the USDA Forest Service and global forestry surveys.
| Tree Species | Typical Mature DBH (cm) | Min DBH (cm) | Max DBH (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quercus robur (English oak) | 70–100 | 30 | 200 |
| Pinus sylvestris (Scots pine) | 50–80 | 25 | 150 |
| Acer saccharum (Sugar maple) | 40–60 | 20 | 100 |
| Fagus grandifolia (American beech) | 60–90 | 30 | 130 |
| Eucalyptus globulus (Blue gum) | 80–120 | 35 | 180 |
| Sequoia sempervirens (Redwood) | 150–350 | 80 | 600 |
| Betula pendula (Silver birch) | 30–50 | 15 | 70 |
| Tectona grandis (Teak) | 60–100 | 35 | 130 |
| Populus tremuloides (Quaking aspen) | 30–60 | 20 | 90 |
| Cedrus deodara (Deodar cedar) | 70–150 | 40 | 250 |
These values help in benchmarking DBH measurements and are commonly used in growth prediction models.
DBH Measurement Standards
DBH is typically measured:
- At 1.3 meters (130 cm) above ground level on the uphill side.
- Using diameter tapes, calipers, or optical dendrometers.
- On single-stemmed trees; special corrections apply for multi-stemmed specimens.
International Standards Referenced:
- FAO Guidelines for National Forest Monitoring (2022)
- US Forest Inventory and Analysis (FIA) DBH protocols
- European National Forest Inventories (ENFI)
DBH Calculator Formulas and Variables Explained
1. Basic DBH from Circumference
- DBH = Diameter at Breast Height (cm)
- C = Circumference at 1.3 m height (cm)
- π (pi) ≈ 3.1416
This is the most direct method, especially when using a diameter tape that reads diameter directly by converting circumference.
2. Basal Area from DBH
- BA = Basal Area in square meters (m²)
- DBH = Diameter at Breast Height (cm)
Basal Area is used to quantify the density of trees in a forest.
3. Volume Estimation Using DBH
- V = Volume of tree (m³)
- F = Form Factor (0.4–0.7, depending on species)
- H = Tree height (m)
- BA = Basal area at breast height (m²)
Common form factors:
- Conifers (conical trees): 0.45–0.55
- Deciduous (broadleaf trees): 0.55–0.65
4. Tree Biomass Estimation
- B = Biomass (kg)
- a, b = Allometric coefficients (species-specific, empirical)
Example coefficients:
- Tropical broadleaf: a = 0.0509, b = 2.46
- Conifer: a = 0.0287, b = 2.62
Source: Chave et al., 2014
5. Carbon Content Estimation
- C = Carbon content (kg)
- 0.47 is the standard coefficient from IPCC guidelines (2006) representing average carbon in tree dry mass.
Extended Table of Calculated DBH Values
Here is a precomputed table converting commonly measured circumferences to DBH and basal area for quick field reference:
| Circumference (cm) | DBH (cm) | Basal Area (m²) |
|---|---|---|
| 31.4 | 10 | 0.0079 |
| 47.1 | 15 | 0.0177 |
| 62.8 | 20 | 0.0314 |
| 78.5 | 25 | 0.0491 |
| 94.2 | 30 | 0.0707 |
| 125.6 | 40 | 0.1257 |
| 157.1 | 50 | 0.1963 |
| 188.5 | 60 | 0.2827 |
| 314.2 | 100 | 0.7854 |
| 471.2 | 150 | 1.7671 |
This table is especially helpful in large-scale field inventories where calculations must be streamlined.
Real-World Applications of DBH Calculations
DBH is a foundational measurement across forestry, conservation biology, ecosystem monitoring, and urban tree management. Below are two detailed real-life case studies showcasing DBH usage and calculation.
Example 1: Estimating Tree Volume and Carbon in a Temperate Forest
Scenario:
A forestry engineer is assessing the volume and carbon content of a Quercus robur (English oak) in a European mixed forest. The tree has:
- Circumference: 125.6 cm
- Tree height: 20 meters
- Form factor (F): 0.55 (broadleaf species)
- Carbon conversion factor: 0.47
Step 1: Calculate DBH
Step 2: Calculate Basal Area (BA)
Step 3: Calculate Tree Volume (V)
Step 4: Estimate Biomass (dry weight)
Average wood density for Quercus robur: 720 kg/m³
Step 5: Calculate Carbon Stored
Conclusion: This single oak tree stores nearly 468 kg of carbon, highlighting its importance in climate mitigation.
Example 2: Urban Tree Assessment for Infrastructure Planning
Scenario:
A municipal arborist is evaluating whether a large Platanus × acerifolia (London Plane tree) near a road should be preserved or relocated during sidewalk expansion. DBH and root zone diameter are critical here.
Measured circumference: 188.5 cm
Height: 17 meters
Species form factor: 0.5
Step 1: DBH Calculation
Step 2: Root Protection Zone (RPZ) Estimate
Standard RPZ radius = 12 × DBH (in inches)
Step 3: Volume & Structural Risk
Conclusion: Given the large volume and 7.2 m RPZ, the tree should be preserved, and construction realigned to avoid root damage.
Why DBH Matters in Forestry and Ecology
DBH data is not only used to estimate tree size and biomass. It forms the basis of broader ecological and management applications:
Applications of DBH in Forestry
- Timber yield estimation
- Stand structure modeling
- Thinning and harvest planning
- Forest growth prediction models
- Remote sensing calibration
Applications of DBH in Ecology
- Carbon cycle modeling
- Species dominance assessments
- Biodiversity correlation studies
- Erosion control strategies in riparian zones
Best Practices and Field Notes
- Avoid defects at 1.3 m (knots, branches, swellings). If present, measure slightly above.
- For leaning trees, always measure along the axis of lean.
- In multi-stemmed trees, measure each stem >10 cm separately and use quadratic mean diameter (QMD).
Tools and Equipment for Accurate DBH Measurement
| Tool | Use Case | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter tape | Standard forestry work | Fast, accurate, direct DBH readout |
| Calipers | Small/medium trees with access | High precision, no need for π |
| Smartphone apps | Urban forestry, citizen science | GPS + DBH estimate, scalable |
| Laser dendrometers | Remote plots, research forests | Combines height + DBH + distance |
Recommended tools:
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions about DBH Calculators
What is the standard height for DBH?
DBH is measured at 1.3 m (4.5 feet) above ground level.
How do I measure DBH on sloped ground?
Measure on the uphill side at 1.3 m from the base.
Is DBH the same as trunk diameter?
Yes, but only when measured at breast height (1.3 m).
Can DBH be used for young trees?
Yes, but many saplings <5 cm DBH are often excluded in commercial inventories.
How does bark thickness affect DBH?
Bark is included in DBH, which is considered an over-bark diameter.