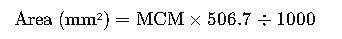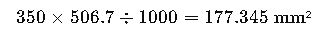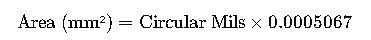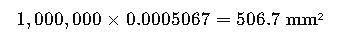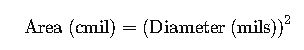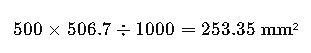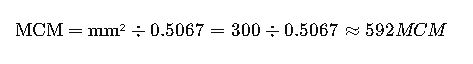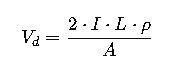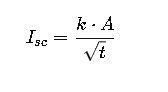The conversion of cable sizes from MCM to square millimeters (mm²) is essential for professionals. MCM is common in North America, while mm² is the global IEC standard unit.
Understanding this conversion is crucial when designing or upgrading electrical systems to ensure compliance, safety, and interoperability across regions and standards.
MCM to mm² Conversion
Comprehensive Table of Common MCM to mm² Conversions
The following table provides a detailed reference of the most commonly used MCM sizes and their equivalent values in square millimeters (mm²). These conversions are based on the exact relationship between circular mils and square millimeters:
Conversion Constant:
1 MCM = 1,000,000 circular mils
1 circular mil = 5.067×10⁻⁴ mm²
1 MCM ≈ 506.7 mm²
| MCM Size | mm² Equivalent | Rounded mm² | Common Use / Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250 MCM | 126.68 mm² | 127 mm² | Industrial feeders, HVAC |
| 300 MCM | 152.01 mm² | 150 mm² | Power distribution panels |
| 350 MCM | 177.35 mm² | 185 mm² | Large motor circuits |
| 400 MCM | 202.68 mm² | 200 mm² | Main service conductors |
| 500 MCM | 253.35 mm² | 250 mm² | Transformers, busbars |
| 600 MCM | 304.02 mm² | 300 mm² | High-capacity feeders |
| 700 MCM | 354.69 mm² | 350 mm² | Substation wiring |
| 750 MCM | 380.03 mm² | 375 mm² | Large utility feeds |
| 800 MCM | 405.36 mm² | 400 mm² | Generator connections |
| 900 MCM | 456.03 mm² | 450 mm² | Utility parallel runs |
| 1000 MCM | 506.7 mm² | 500 mm² | Large-scale installations |
| 1250 MCM | 633.38 mm² | 630 mm² | Power generation |
| 1500 MCM | 760.05 mm² | 750 mm² | Large infrastructure cables |
| 1750 MCM | 886.73 mm² | 875 mm² | Specialized industrial needs |
| 2000 MCM | 1013.4 mm² | 1000 mm² | Utility high-voltage lines |
Note: Rounding conventions may vary slightly between manufacturers, especially for cable sizing nearest to standardized IEC mm² sizes (e.g., 240 mm², 300 mm², etc.).
Conversion Formulas and Technical Explanation
The relationship between MCM and mm² is rooted in geometry and metric conversion factors. Below are all the essential formulas and an explanation of each variable.
Formula #1: Basic Conversion
Where:
- MCM: Thousands of circular mils
- 506.7: The number of mm² in one MCM (1 MCM = 1,000,000 circular mils × 0.0005067 mm²/cmil)
- 1000: Converts thousands to standard units
Example:
Convert 350 MCM to mm²:
Formula #2: From Circular Mils (CM) Directly to mm²
Where:
- Circular Mils = MCM × 1,000,000
- 0.0005067: Conversion factor from circular mil to mm²
Example:
Convert 1,000,000 cmil (i.e., 1 MCM) to mm²:
Understanding Circular Mils
A circular mil (cmil) is defined as the area of a circle with a diameter of one mil (0.001 inches). The formula is:
This is a non-metric unit, so conversion requires attention to significant figures, especially in international applications.
Real-World Application Examples
Below are two practical use cases demonstrating how to apply MCM to mm² conversions in real-world electrical engineering scenarios.
Case Study 1: Upgrading an Industrial Feeder System (NEMA → IEC)
Scenario:
A manufacturing facility in the U.S. is expanding operations to Europe. It uses 500 MCM cables for primary feeders and needs to determine the mm² equivalent for IEC-compliant installations.
Step-by-Step Calculation:
- Given: 500 MCM
- Use Formula:
- Closest IEC standard size: 250 mm²
Result:
For compliance with IEC standards, 500 MCM should be replaced with 250 mm² cable with equivalent ampacity rating.
Why It Matters:
Matching the conductor size ensures correct current-carrying capacity and avoids overheating or non-compliance with local codes such as IEC 60228.
Case Study 2: Cross-Border Solar Plant Cabling Design
Scenario:
An engineering firm is designing a 5 MW solar installation that spans from Mexico (IEC-standard) to the southern U.S. (NEMA-standard). The conductor used in the Mexican side is 300 mm², and the goal is to match the conductor sizing in the U.S. side with MCM.
Step-by-Step Calculation:
- Given: 300 mm²
- Convert to MCM using inverse of Formula #1:
Result:
Use 600 MCM conductors in the U.S. to match the 300 mm² IEC conductors in Mexico.
Code Considerations:
- Confirm the ampacity under both NEC Table 310.16 and IEC 60364.
- Account for temperature derating and installation methods (e.g., underground or tray).
Extended MCM to mm² Conversion Table with Ampacity Ratings
Beyond simple dimensional conversions, understanding how ampacity (the current a conductor can carry safely) varies across conductor sizes is crucial. Ampacity depends on conductor material (copper or aluminum), insulation type (e.g., THHN, XHHW), and installation environment (ambient temperature, conduit type).
The table below includes:
- MCM size
- mm² equivalent
- Approximate ampacity (from NEC Table 310.16 at 75°C, copper, 3 conductors in raceway or cable)
Always consult local codes for derating factors (e.g., NEC adjustment for more than three current-carrying conductors or high ambient temperature).
| MCM | mm² | Ampacity (Copper, 75°C) | Typical IEC Equivalent | IEC Ampacity (Ref. IEC 60364) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 250 | 127 | 255 A | 120 mm² | ~260 A |
| 300 | 152 | 285 A | 150 mm² | ~290 A |
| 350 | 177 | 310 A | 185 mm² | ~320 A |
| 400 | 203 | 335 A | 200 mm² | ~340 A |
| 500 | 253 | 380 A | 240–250 mm² | ~400 A |
| 600 | 304 | 420 A | 300 mm² | ~450 A |
| 700 | 355 | 460 A | 350 mm² | ~500 A |
| 750 | 380 | 475 A | 375 mm² | ~520 A |
| 800 | 405 | 490 A | 400 mm² | ~540 A |
| 900 | 456 | 520 A | 450 mm² | ~570 A |
| 1000 | 507 | 545 A | 500 mm² | ~600 A |
Important Notes:
- IEC ampacity is derived from IEC 60364 and HD 60364-5-52 guidelines.
- NEC ampacity is from the 2023 National Electrical Code, Table 310.16.
- Ampacity varies with installation method: duct bank, tray, conduit, direct burial, etc.
Regulatory Standards and Normative References
Correct sizing is more than just a conversion — it’s about compliance. Engineers and electricians must reference national or international standards depending on jurisdiction.
Key Regulatory Bodies and Standards
| Standard | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| NEC (NFPA 70) | U.S. National Electrical Code – conductor sizing and ampacity tables | NFPA NEC Code |
| IEC 60228 | International standard for conductor sizes and resistance | IEC 60228 Summary |
| IEC 60364-5-52 | Installation standards for low-voltage wiring | IEC 60364 Overview |
| IEEE 835 | Standard for cable ampacity (especially for utilities) | IEEE Xplore |
Engineering Considerations in Practice
1. Voltage Drop Calculations
Using the converted mm² size, you must ensure the cable will maintain acceptable voltage drop limits (typically <3% for feeders and <5% total). Voltage drop formulas are dependent on conductor cross-section:
Where:

Use proper area (from mm² after MCM conversion) to plug into this equation.
2. Short Circuit Withstand Capacity
Cables must withstand short-circuit currents for the maximum clearing time of the protection device. IEC and IEEE standards provide this calculation:
Where:

3. Cable Derating and Grouping Factors
In both IEC and NEC contexts, conductors bundled together (more than three) require derating:
- NEC Table 310.15(C)(1): Ampacity derating for >3 conductors in raceway
- IEC 60364 Annex B: Correction factors based on grouping and ambient conditions
Always apply these to the base ampacity calculated after size conversion.
When to Use MCM vs. mm²: Global Engineering Practice
| Application Region | Standard | Preferred Unit | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States, Canada | NEC/NEMA | MCM | Use MCM for local design |
| Europe, Asia, Latin America | IEC | mm² | Convert to mm² for specification |
| Global projects (e.g., oil & gas, mining) | Dual | Both | Specify both for clarity |
For example, in global tenders, it’s common to write:
“500 MCM copper conductor (equivalent to approx. 250 mm²) per IEC 60228 Class 2.”
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I use the exact mm² equivalent of an MCM value?
Not always. Standard mm² sizes under IEC (e.g., 120 mm², 150 mm², 185 mm²…) don’t always line up precisely. Select the closest higher standard size for safety and compliance.
Are MCM and kcmil the same?
Yes. MCM = kcmil = 1,000 circular mils. The terms are interchangeable in modern engineering texts.
What’s the impact of insulation type?
Insulation impacts ampacity. For example, XHHW has higher temperature rating than THHN, allowing greater current in same size.