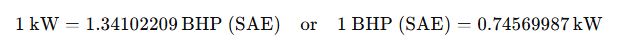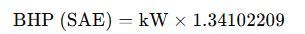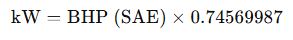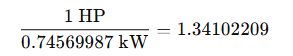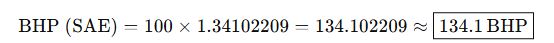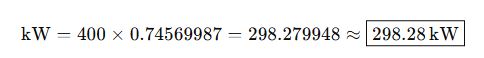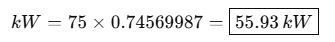The conversion between kilowatts (kW) and brake horsepower (BHP) is essential in mechanical and automotive engineering.
BHP (SAE) allows engine comparisons according to standards like SAE J1349, ISO 1585, and DIN 70020
kW ↔ BHP Calculator (SAE)
Common Conversion Values – kW to BHP (SAE) and Vice Versa
The standard formula used for this conversion is:
Below is an extensive conversion table of commonly used power ratings for motors and engines.
Conversion Table: kW ↔ BHP (SAE)
| Kilowatts (kW) | Brake Horsepower (BHP, SAE) | BHP Rounded |
|---|---|---|
| 0.75 | 1.006 | 1.01 |
| 1 | 1.341 | 1.34 |
| 2 | 2.682 | 2.68 |
| 3 | 4.023 | 4.02 |
| 5 | 6.705 | 6.71 |
| 7.5 | 10.058 | 10.06 |
| 10 | 13.410 | 13.41 |
| 15 | 20.115 | 20.12 |
| 20 | 26.820 | 26.82 |
| 30 | 40.230 | 40.23 |
| 50 | 67.051 | 67.05 |
| 75 | 100.576 | 100.58 |
| 100 | 134.102 | 134.10 |
| 150 | 201.153 | 201.15 |
| 200 | 268.204 | 268.20 |
| 250 | 335.255 | 335.26 |
| 300 | 402.306 | 402.31 |
| 500 | 670.511 | 670.51 |
These values are especially common in:
- Automotive engine specifications (internal combustion and electric)
- Diesel generators and industrial motors
- Pumps, compressors, and HVAC equipment
- Marine propulsion systems
Conversion Formulas and Detailed Variable Explanation
Standard SAE Conversion Formula:
Variables:
- BHP (SAE) = Brake horsepower as defined by SAE J1349 (net power at the crankshaft)
- kW = Kilowatts, the SI unit for power (1 kW = 1000 watts)
This conversion is based on mechanical horsepower (550 ft-lbf/s), and SAE J1349 includes accessory loads such as water pump, alternator, and emissions equipment, making it closer to real-world performance than older gross horsepower ratings.
Reverse Conversion:
Why Use These Specific Factors?
- 1 horsepower (mechanical) = 745.69987 watts exactly.
- The factor 1.34102209 derives from:
It’s vital to distinguish SAE net BHP from DIN, ISO, or JIS horsepower definitions, as they may vary in the accounting of auxiliary systems, ambient conditions, and test standards.
Real-World Examples – Application of kW ↔ BHP Conversion
Example 1: Automotive Engine Specification
Problem:
An imported electric vehicle lists its motor output as 100 kW. What is its equivalent BHP (SAE) for marketing in the U.S.?
Solution:
Use Case:
This conversion allows automakers to adjust specifications on spec sheets or advertising materials for compliance with SAE J1349 and U.S. consumer expectations.
Example 2: Industrial Generator Rating
Problem:
A facility in Europe has a diesel generator rated at 400 BHP (SAE). What is the equivalent power in kilowatts for specifying compatible equipment under IEC standards?
Solution:
Use Case:
In international projects, converting to kW ensures consistency with IEC 60034 standard motor efficiencies, grid compatibility, and compliance documentation.
Engineering Standards and Guidelines
When using or interpreting kW and BHP values, it is essential to refer to current technical standards. The most relevant include:
- SAE J1349: Engine Power Test Code – Spark Ignition and Diesel Engines
- ISO 1585: Road vehicles — Engine test code — Net power
- DIN 70020: German standard for horsepower ratings
- IEC 60034: Rotating electrical machines — Part 1: Rating and performance
Practical Notes and Engineering Considerations
When to Use kW vs. BHP
- Use kW:
- For IEC-based electrical design and engineering documentation
- In electric motors and energy consumption evaluations
- Use BHP (SAE):
- In North American automotive, marine, or aviation sectors
- When referencing performance in advertising or user manuals for ICE engines
Advanced Applications in Industry
The conversion between kW and BHP (SAE) is not just mathematical — it directly impacts engineering design, procurement, maintenance planning, and compliance reporting. Below are advanced sector-specific applications.
Electrical Motor Specification
In industrial installations, motors are typically rated in kilowatts per IEC 60034. However, vendors or OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) may provide BHP-based specifications, particularly in North America.
Example:
A centrifugal pump requires a motor with 75 BHP continuous rating. The equivalent in kW:
Note: Always add a safety margin (e.g., 10–15%) in mechanical and electrical power sizing to accommodate startup currents and torque load spikes.
Aerospace and Marine Propulsion
In the aviation and marine sectors, BHP is a critical rating that defines the maximum shaft output available to drive propellers or turbines. These applications must consider:
- Altitude correction factors (aviation)
- Water density and thrust curve correction (marine)
- Conversion to metric units for integration with fuel flow (L/h) and efficiency (g/kWh) calculations
Common Mistakes in kW ↔ BHP Conversion
Avoid these pitfalls when working with conversions:
- Confusing Gross vs. Net Horsepower:
- SAE J1349 defines net power including accessories.
- SAE J1995 or DIN 70020 may define gross power (idealized).
- Using Rounded Factors:
- Avoid using 1.34 or 0.75 for quick estimates in precision-critical applications.
- Overlooking Ambient Correction Standards:
- ISO 3046 and SAE J1349 define ambient conditions (25°C, 100 kPa pressure, etc.). Deviating from these alters real output.
Integrating a Dynamic Calculator on Your Website
Why Build a Web-Based kW ↔ BHP (SAE) Calculator?
A web-based calculator:
- Enhances UX for engineers and students
- Supports global conversions across different unit systems
- Increases your site’s SEO performance and dwell time
External Resources and Authoritative References
To ensure compliance and further your research, consult the following:
- SAE International (J1349 Standard):
https://www.sae.org/standards/content/j1349_201106/ - International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC 60034):
https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/2612 - National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) Motor Database:
https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy19osti/72778.pdf - Conversion Guidelines – RapidTables:
https://www.rapidtables.com/convert/power/kw-to-hp.html - ISO 1585 Engine Test Code:
https://www.iso.org/standard/34333.html