Understanding precipitation measurement and conversion into hydrological units is crucial for meteorology, hydrology, agriculture, and water resources. Transforming precipitation depth in millimeters into liters per square meter enables volume analysis for irrigation and infrastructure.
Precipitation Converter — mm to liters per m²
Quickly convert rainfall depth (mm) to liters per square metre (L/m²). Total volume automatically calculated while you type.
How does this conversion work?
Why include area?
Understanding Precipitation Units
- Millimeters (mm):
In meteorology, rainfall depth is commonly measured in millimeters. For example, 10 mm of rain means that if the rainfall were uniformly distributed and not absorbed or evaporated, it would form a layer of water 10 mm deep over a flat surface. - Liters per Square Meter (L/m²):
This unit represents the volume of water collected per square meter of surface area. It provides a direct link between rainfall depth and usable water volume, particularly relevant for irrigation, drainage, and water harvesting systems.
Key principle:
1 mm of rainfall = 1 L/m² of water.
This equivalence is due to the relationship between length, volume, and area in the metric system. We’ll prove and expand this equivalence using formulas.
Core Formula for Conversion
The fundamental formula connecting precipitation depth and volume is:
V=h×A
Where:
- V= Volume of water (liters, L)
- h= Precipitation depth (millimeters, mm)
- A= Area receiving rainfall (square meters, m²)
Since 1 mm = 0.001 m, the formula in cubic meters becomes:

Detailed Explanation of Variables
- Precipitation depth (h):
- Typical daily rainfall events range between 0.1 mm (light drizzle) and 50–100 mm (heavy storms).
- Extreme weather events may exceed 200–300 mm in 24 hours, especially in tropical or monsoon regions.
- Area (A):
- Conversion is usually expressed per 1 m² for simplicity.
- However, in practical hydrology, areas are extended to hectares (10,000 m²) or catchments (km²) for volume estimation.
- Volume (V):
- Provides the water collected in liters for given rainfall and area.
- Used to calculate reservoir inflows, runoff potential, irrigation volumes, and roof water harvesting capacity.
Extensive Conversion Table: Precipitation (mm → L/m²)
The following table provides common rainfall depths and their direct equivalence to liters per square meter.
| Rainfall Depth (mm) | Water Volume (L/m²) | Rainfall Classification (WMO Standard) | Equivalent Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 mm | 0.1 L/m² | Very light drizzle | Barely measurable |
| 0.5 mm | 0.5 L/m² | Light drizzle | Thin surface wetting |
| 1 mm | 1 L/m² | Light rain | Minimum for irrigation records |
| 2 mm | 2 L/m² | Light rain | Common short shower |
| 5 mm | 5 L/m² | Moderate rain | Garden irrigation equivalent |
| 10 mm | 10 L/m² | Moderate rain | Typical daily rainfall |
| 20 mm | 20 L/m² | Heavy rain | Street flooding possible |
| 30 mm | 30 L/m² | Heavy rain | Saturation of soil layers |
| 50 mm | 50 L/m² | Very heavy rain | Flash flood threshold |
| 75 mm | 75 L/m² | Severe rainfall | Drainage system overload |
| 100 mm | 100 L/m² | Extreme rainfall | Common in hurricanes |
| 150 mm | 150 L/m² | Extreme rainfall | River flood level |
| 200 mm | 200 L/m² | Catastrophic event | Tropical cyclone scale |
| 300 mm | 300 L/m² | Catastrophic rainfall | Rare but possible in monsoons |
Extended Conversion for Larger Areas
To scale rainfall volumes over larger areas:
V=h×A
Example Extended Table: Rainfall Volumes over Different Surfaces
| Rainfall (mm) | 100 m² Roof (L) | 1 Hectare (10,000 m²) (L) | 1 km² Catchment (L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mm | 100 L | 10,000 L (10 m³) | 1,000,000 L (1,000 m³) |
| 10 mm | 1,000 L | 100,000 L (100 m³) | 10,000,000 L (10,000 m³) |
| 50 mm | 5,000 L | 500,000 L (500 m³) | 50,000,000 L (50,000 m³) |
| 100 mm | 10,000 L | 1,000,000 L (1,000 m³) | 100,000,000 L (100,000 m³) |
| 200 mm | 20,000 L | 2,000,000 L (2,000 m³) | 200,000,000 L (200,000 m³) |
This scaling is critical for rainwater harvesting design, flood prediction, and hydrological modeling.
Real-World Applications
Case Study 1: Rainwater Harvesting on a Residential Roof
- Problem:
A house has a roof area of 120 m². During a storm, 25 mm of rainfall is recorded. How much water can be harvested? - Solution:
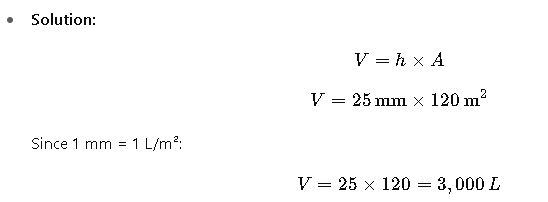
- Interpretation:
The storm can provide 3 cubic meters of water, enough to cover domestic non-potable needs for several days.
Case Study 2: Flood Estimation in a Small Catchment
- Problem:
A catchment area of 5 km² receives a rainfall event of 60 mm in 12 hours. Estimate the total precipitation volume.
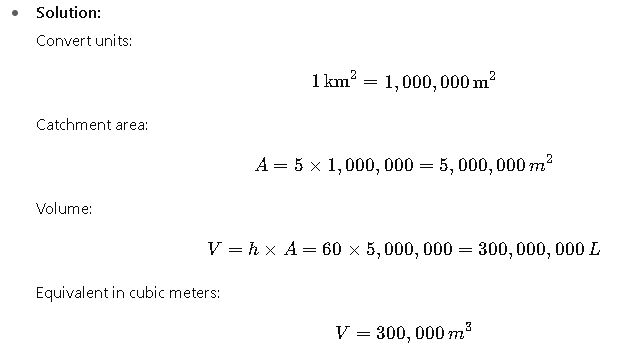
- Interpretation:
Such rainfall may cause flash flooding if drainage capacity is insufficient. Hydrologists use this conversion in flood risk models.
Practical Applications of Precipitation Conversion in Engineering and Science
The conversion of rainfall depth into liters per square meter is not only a matter of simple arithmetic but a fundamental step in hydrological engineering, urban planning, and environmental sciences. By expressing rainfall in terms of volume per area, professionals can bridge the gap between meteorological data and practical design parameters.
Applications in Hydrology and Water Resource Management
- Runoff Estimation: Hydrologists use rainfall depth converted into water volume to calculate how much surface runoff will flow into rivers, reservoirs, or drainage systems.
- Flood Modeling: Extreme precipitation events measured in liters per square meter can be scaled across large catchment areas to estimate flood peaks.
- Groundwater Recharge: By converting precipitation into water volume, hydrogeologists can estimate how much water percolates into aquifers.
- Reservoir Inflows: Storage planning for dams and reservoirs requires converting incoming precipitation into potential water inflows.
Applications in Agriculture and Irrigation
- Irrigation Scheduling: Farmers use rainfall data in liters per square meter to determine whether additional irrigation is needed.
- Crop Water Requirement Analysis: The total rainfall volume can be directly compared to crop evapotranspiration values.
- Soil Moisture Balances: Converted precipitation values help estimate how much water infiltrates into the root zone.
- Water Harvesting Systems: Rainwater stored from roof catchments or farm ponds is calculated directly in liters based on rainfall events.
Applications in Urban and Civil Engineering
- Stormwater Drainage Design: Urban engineers require rainfall expressed in water volume to size drainage pipes and detention basins.
- Green Infrastructure Planning: Rain gardens, permeable pavements, and bioswales are designed based on precipitation-to-volume conversions.
- Floodproofing Buildings: Roof runoff and ground infiltration loads are calculated per square meter in liters to design waterproofing systems.
- Water Supply for Cities: Municipal rainwater harvesting initiatives rely on accurate precipitation volume conversions to assess feasibility.
Expanded Conversion Tables for Real-World Scenarios
To improve readability, here are specialized conversion tables for different professional uses.
Rainfall to Water Supply for Household Roofs
| Rainfall (mm) | 50 m² Roof (L) | 100 m² Roof (L) | 200 m² Roof (L) | 500 m² Roof (L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mm | 250 L | 500 L | 1,000 L | 2,500 L |
| 10 mm | 500 L | 1,000 L | 2,000 L | 5,000 L |
| 25 mm | 1,250 L | 2,500 L | 5,000 L | 12,500 L |
| 50 mm | 2,500 L | 5,000 L | 10,000 L | 25,000 L |
| 100 mm | 5,000 L | 10,000 L | 20,000 L | 50,000 L |
This table shows how a single storm event can produce significant water volumes, enough to cover domestic use, irrigation, or storage systems.
Rainfall Volumes Across Agricultural Land
| Rainfall (mm) | 1 Hectare (10,000 m²) | 5 Hectares | 10 Hectares | 50 Hectares |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mm | 100,000 L | 500,000 L | 1,000,000 L | 5,000,000 L |
| 25 mm | 250,000 L | 1,250,000 L | 2,500,000 L | 12,500,000 L |
| 50 mm | 500,000 L | 2,500,000 L | 5,000,000 L | 25,000,000 L |
| 100 mm | 1,000,000 L | 5,000,000 L | 10,000,000 L | 50,000,000 L |
This perspective is crucial for farmers, agronomists, and water managers, showing how precipitation translates into actual water availability for crops and soil recharge.
Real-World Example 3: Urban Stormwater Drainage Design
Imagine a city block of 2 hectares. A rainstorm delivers 40 mm of precipitation in just two hours. When converted into liters per square meter, engineers can quickly calculate that the total water load on the drainage system will exceed 800,000 liters. Without proper conversion, designers might underestimate pipe diameters, resulting in urban flooding.
This type of calculation underpins sustainable urban drainage systems (SUDS) and modern smart-city infrastructure.
Real-World Example 4: Irrigation Planning in Semi-Arid Regions
A farmer in a semi-arid zone manages 20 hectares of farmland. Seasonal rainfall averages 350 mm. By converting this rainfall into liters per square meter and scaling across the land, the farmer estimates that the annual water input is 70 million liters.
This helps determine whether rainfall alone is sufficient for crop growth or whether supplemental irrigation must be provided. The conversion also allows comparisons with crop evapotranspiration requirements, ensuring efficient water use.
Advanced Considerations for Precipitation Conversion
Evaporation and Interception
Not all rainfall reaching the ground contributes to usable water. Losses occur due to:
- Evaporation during rainfall events
- Interception by vegetation canopy
- Surface storage on leaves, soil crusts, or pavements
Therefore, engineers often adjust precipitation values using loss factors before final calculations.
Infiltration and Runoff Ratios
Converted precipitation volumes must be separated into:
- Infiltrated water contributing to groundwater recharge
- Surface runoff leading to rivers, lakes, or drainage networks
- Soil retention available for crops
These ratios depend on soil type, slope, land use, and rainfall intensity.
Design Standards and Norms
Various international standards provide guidelines for precipitation analysis:
- World Meteorological Organization (WMO): Classification of rainfall intensities and observation standards.
- FAO Irrigation Guidelines: Linking precipitation with crop water requirements.
- ISO 772: Hydrometry Standards: Definitions of hydrological terms and units.
- Local Building Codes: Drainage and flood-proofing design criteria.
These standards emphasize the need for precise unit conversion to ensure safe and efficient infrastructure design.