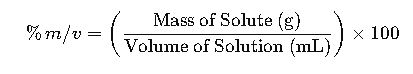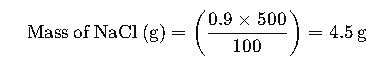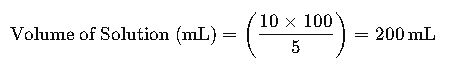Mass/volume percentage (% m/v) quantifies solute mass relative to solution volume for accurate concentrations. It ensures precision in chemistry, pharmaceuticals, food industry, and laboratory applications worldwide reliably.
Mass/Volume Percentage (% m/v) Calculator
How is % m/v calculated?
What is considered a valid input?
Common Mass/Volume Percentage Values
The mass/volume percentage (% m/v) is a standard unit of concentration used to express the amount of solute in a solution. Below is a table showcasing common % m/v values and their typical applications:
| Mass of Solute (g) | Volume of Solution (mL) | % m/v (%) | Application Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 1 | Saline solution for medical use |
| 5 | 100 | 5 | Laboratory buffer preparation |
| 10 | 500 | 2 | Glucose solution for cell culture |
| 0.9 | 100 | 0.9 | Physiological saline (normal saline) |
| 20 | 1000 | 2 | Antiseptic solution concentration |
| 15 | 750 | 2 | Pharmaceutical solution preparation |
| 50 | 1000 | 5 | Industrial cleaning solution |
| 2 | 200 | 1 | Food additive concentration |
| 25 | 500 | 5 | Laboratory reagent solution |
| 0.5 | 50 | 1 | Cosmetic product formulation |
Formulas and Detailed Explanation
The primary formula for calculating mass/volume percentage is:
Variables:
- Mass of Solute (g): The weight of the solute dissolved in the solution, measured in grams.
- Volume of Solution (mL): The total volume of the solution, including both solute and solvent, measured in milliliters.
Common Values:
- Mass of Solute: Typically ranges from milligrams to several grams, depending on the desired concentration.
- Volume of Solution: Ranges from milliliters to liters, depending on the scale of the preparation.
Rearranged Formulas:
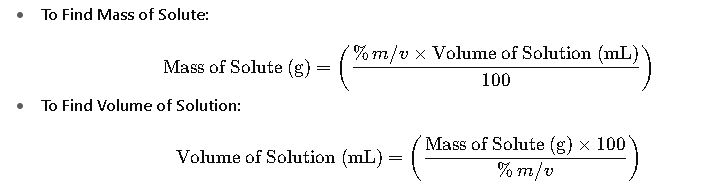
Real-World Examples
Example 1: Preparing a 0.9% m/v Saline Solution
Problem: How much NaCl is needed to prepare 500 mL of a 0.9% m/v saline solution?
Solution:
- Given: % m/v = 0.9%, Volume = 500 mL
- Using the formula:
Example 2: Determining the Volume of Solution from Mass of Solute
Problem: What volume of solution is required to achieve a 5% m/v concentration with 10 g of NaCl?
Solution:
- Given: Mass of NaCl = 10 g, % m/v = 5%
- Using the formula:
Common Concentrations in Different Industries
The mass/volume percentage (% m/v) is widely used across healthcare, pharmaceuticals, food industry, and laboratories. The following table summarizes commonly encountered concentrations and their typical uses:
| % m/v | Example Solute | Typical Application | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9 | NaCl | Physiological saline | Used in IV drips and wound irrigation |
| 1 | Glucose | Oral rehydration solution | Mildly sweet, isotonic solution |
| 2 | Ethanol | Disinfectant solution | Standard laboratory cleaning solution |
| 5 | NaCl | Lab buffer preparation | Common in molecular biology protocols |
| 10 | Glucose | Cell culture media | Provides energy source for cells |
| 15 | Hydrogen Peroxide | Antiseptic solution | Used in low concentration for wound cleaning |
| 20 | Sucrose | Food and beverage solutions | Used in syrup and confectionery |
| 50 | NaOH | Industrial cleaning | Highly concentrated solution for heavy-duty cleaning |
This table illustrates that % m/v is versatile, allowing precise adjustment of solute concentrations for specific applications.
Factors Affecting % m/v in Practice
- Solute Type
Different solutes dissolve differently in a given solvent. Ionic compounds like NaCl dissolve readily in water, whereas larger organic molecules may require heating or special solvents. - Volume Precision
The final volume of solution is critical. Adding solute increases the total volume slightly, so measuring after dissolution ensures accuracy. - Temperature and Solubility
Temperature can affect solubility. Some compounds dissolve better at higher temperatures, while others may precipitate if the solution cools. - Application Purpose
In medical applications, accuracy is essential for patient safety. In industrial processes, small deviations might be acceptable, but they can affect efficiency.
Real-World Applications of % m/v
Case Study 1: Medical Saline Solution
A hospital needs 1 liter of 0.9% m/v NaCl solution for IV administration. This is standard “normal saline.”
Application Insights:
- Used to hydrate patients, restore electrolytes, and maintain blood volume.
- Accuracy is crucial: too much NaCl can cause hypernatremia; too little is ineffective.
- Pharmacy technicians use pre-calculated tables to weigh solutes quickly and ensure patient safety.
Case Study 2: Food Industry – Syrup Preparation
A candy manufacturer needs a 20% m/v sucrose solution to produce syrup for candies.
Application Insights:
- Ensures consistent sweetness and texture.
- % m/v helps adjust recipes for different batch sizes.
- Lab technicians often prepare small test batches to verify consistency before scaling production.
Tips for Accurate Mass/Volume Preparation
- Always use calibrated balances and volumetric flasks.
- Dissolve solute completely before adjusting the final volume.
- Label solutions with % m/v and preparation date to avoid errors.
- Document all steps for traceability in laboratory or industrial environments.
Benefits of Understanding % m/v
- Precision: Enables exact control over solution properties.
- Safety: Critical in pharmaceuticals and medical solutions.
- Efficiency: Reduces waste and ensures consistent product quality.
- Versatility: Applicable in chemistry, biology, food, and industrial processes.