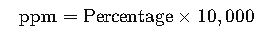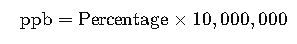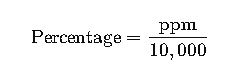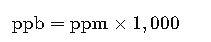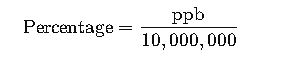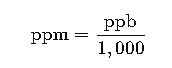Accurate concentration conversions between ppm, ppb, and percent are critical in scientific applications. These conversions ensure precise chemical measurements, environmental monitoring, and industrial process control worldwide.
Concentration Conversion Calculator
How are the conversions calculated?
Why use this calculator?
Concentration Conversion Table
Below is an extensive table illustrating the relationships between percentage (%), parts per million (ppm), and parts per billion (ppb). This table is designed to facilitate quick conversions and enhance understanding of concentration units.
| Percentage (%) | Parts per Million (ppm) | Parts per Billion (ppb) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0000001 | 1 | 1,000 |
| 0.000001 | 10 | 10,000 |
| 0.00001 | 100 | 100,000 |
| 0.0001 | 1,000 | 1,000,000 |
| 0.001 | 10,000 | 10,000,000 |
| 0.01 | 100,000 | 100,000,000 |
| 0.1 | 1,000,000 | 1,000,000,000 |
| 1 | 10,000,000 | 10,000,000,000 |
Note: 1 ppm = 1 mg/L = 1 mg/kg = 1 µg/g
Formulas for Concentration Conversions
Understanding the formulas for converting between percentage, ppm, and ppb is crucial for accurate calculations:
1. Percentage to ppm Conversion
Example: 0.01% = 0.01 × 10,000 = 100 ppm
2. Percentage to ppb Conversion
Example: 0.01% = 0.01 × 10,000,000 = 100,000 ppb
3. ppm to Percentage Conversion
Example: 100 ppm = 100 ÷ 10,000 = 0.01%
4. ppm to ppb Conversion
Example: 100 ppm = 100 × 1,000 = 100,000 ppb
5. ppb to Percentage Conversion
Example: 100,000 ppb = 100,000 ÷ 10,000,000 = 0.01%
6. ppb to ppm Conversion
Example: 100,000 ppb = 100,000 ÷ 1,000 = 100 ppm
Detailed Explanation of Variables
- Percentage (%): Represents the number of parts of solute per 100 parts of solution.
- ppm (Parts per Million): Denotes the number of parts of solute per million parts of solution.
- ppb (Parts per Billion): Indicates the number of parts of solute per billion parts of solution.
Real-World Examples
Example 1: Environmental Monitoring
Scenario: Monitoring the concentration of lead (Pb) in drinking water.
- Given: Lead concentration = 15 ppb
- Objective: Convert to ppm and percentage.
Solution:
- 15 ppb = 15 ÷ 1,000 = 0.015 ppm
- 0.015 ppm = 0.015 ÷ 10,000 = 0.00015%
Interpretation: A concentration of 15 ppb of lead is equivalent to 0.015 ppm or 0.00015%.
Example 2: Industrial Application
Scenario: Determining the concentration of a chemical solvent in a manufacturing process.
- Given: Solvent concentration = 0.5%
- Objective: Convert to ppm and ppb.
Solution:
- 0.5% = 0.5 × 10,000 = 5,000 ppm
- 5,000 ppm = 5,000 × 1,000 = 5,000,000 ppb
Interpretation: A concentration of 0.5% is equivalent to 5,000 ppm or 5,000,000 ppb.
Additional Considerations
- Density of Solvent: When dealing with solutions where the solvent’s density differs from water, adjustments may be necessary. For instance, in organic solvents, the density can vary significantly, affecting the conversion factors.
- Temperature and Pressure: For gases, temperature and pressure conditions can influence the volume and, consequently, the concentration measurements. Standard conditions (STP) are often assumed unless specified otherwise.
- Unit Consistency: Always ensure that the units of mass and volume are consistent when performing conversions.
Conclusion
Understanding and accurately converting between percentage, ppm, and ppb are essential skills in various fields, including environmental science, chemistry, and industrial processes. By mastering the formulas and applying them to real-world scenarios, professionals can ensure precise measurements and maintain compliance with regulatory standards.